Regulatory Cross Talk Between SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding and Replication Machinery in the Human Host
- PMID: 32695025
- PMCID: PMC7338756
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00802
Regulatory Cross Talk Between SARS-CoV-2 Receptor Binding and Replication Machinery in the Human Host
Abstract
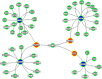
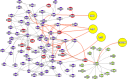
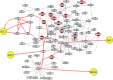
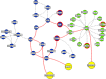
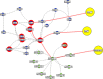
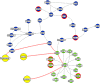
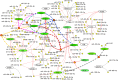
We dissect the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 in human lung host from the initial phase of receptor binding to viral replication machinery. Two independent lung protein interactome were constructed to reveal the signaling process on receptor activation and host protein hijacking machinery in the pathogenesis of virus. Further, we test the functional role of the hubs derived from the interactome. Most hubs proteins were differentially regulated on SARS-CoV-2 infection. Also, the proteins in viral replication hubs were related with cardiovascular disease, diabetes and hypertension confirming the vulnerability and severity of infection in the risk individual. Additionally, the hub proteins were closely linked with other viral infection, including MERS and HCoVs which suggest similar infection pattern in SARS-CoV-2. We identified five hubs that interconnect both networks that show the preparation of optimal environment in the host for viral replication process upon receptor attachment. Interestingly, we propose that seven potential miRNAs, targeting the intermediate phase that connects receptor and viral replication process a better choice as a drug for SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: Covid-19; SARS-CoV-2; host mechanism; miRNA targets; systems biology; transcriptome.
Copyright © 2020 Ahmed, Paramasivam, Raj, Kumar, Murugesan and Ramakrishnan.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Epigenetic Regulator miRNA Pattern Differences Among SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, and SARS-CoV-2 World-Wide Isolates Delineated the Mystery Behind the Epic Pathogenicity and Distinct Clinical Characteristics of Pandemic COVID-19.Front Genet. 2020 Jul 10;11:765. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00765. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32765592 Free PMC article.
-
Computational analysis of microRNA-mediated interactions in SARS-CoV-2 infection.PeerJ. 2020 Jun 5;8:e9369. doi: 10.7717/peerj.9369. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 32547891 Free PMC article.
-
A Kinome-Wide Small Interfering RNA Screen Identifies Proviral and Antiviral Host Factors in Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Replication, Including Double-Stranded RNA-Activated Protein Kinase and Early Secretory Pathway Proteins.J Virol. 2015 Aug;89(16):8318-33. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01029-15. Epub 2015 Jun 3. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26041291 Free PMC article.
-
Host DDX Helicases as Possible SARS-CoV-2 Proviral Factors: A Structural Overview of Their Hijacking Through Multiple Viral Proteins.Front Chem. 2020 Dec 10;8:602162. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.602162. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 33381492 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Through DNA sensors and hidden mitochondrial effects of SARS-CoV-2.J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2021 Aug 23;27:e20200183. doi: 10.1590/1678-9199-JVATITD-2020-0183. eCollection 2021. J Venom Anim Toxins Incl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 34471404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tiotropium is Predicted to be a Promising Drug for COVID-19 Through Transcriptome-Based Comprehensive Molecular Pathway Analysis.Viruses. 2020 Jul 20;12(7):776. doi: 10.3390/v12070776. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32698440 Free PMC article.
-
Multiomics integration-based molecular characterizations of COVID-19.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Jan 17;23(1):bbab485. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab485. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 34864875 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nucleic Acid-Based COVID-19 Therapy Targeting Cytokine Storms: Strategies to Quell the Storm.J Pers Med. 2022 Mar 3;12(3):386. doi: 10.3390/jpm12030386. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35330388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution, Ecology, and Zoonotic Transmission of Betacoronaviruses: A Review.Front Vet Sci. 2021 May 20;8:644414. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.644414. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34095271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MSC-derived exosomes carrying a cocktail of exogenous interfering RNAs an unprecedented therapy in era of COVID-19 outbreak.J Transl Med. 2021 Apr 22;19(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02840-3. J Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33888147 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chan J. F., Kok K. H., Zhu Z., Chu H., To K. K., Yuan S., et al. (2020). Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 221–236. 10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

