FKS1 mutation associated with decreased echinocandin susceptibility of Aspergillus fumigatus following anidulafungin exposure
- PMID: 32686741
- PMCID: PMC7371691
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-68706-8
FKS1 mutation associated with decreased echinocandin susceptibility of Aspergillus fumigatus following anidulafungin exposure
Abstract
Invasive aspergillosis (IA) is a potentially lethal infection that affects mostly immunocompromised patients caused by Aspergillus fumigatus. Echinocandins are a second-line therapy against IA, used as a salvage therapy as well as for empirical or prophylactic therapy. Although they cause lysis of growing hyphal tips, they are considered fungistatic against molds. In vivo echinocandins resistance is uncommon; however, its wide clinical use could shortly lead to the emergence of A. fumigatus resistance. The aims of the present work was to assess the development of reduced echinocandins susceptibility phenotype by a A. fumigatus strain and to unveil the molecular mechanism underlying such phenotype. We induced in vitro cross-resistance to echinocandins following exposure of A. fumigatus to anidulafungin. Stability of the resistant phenotype was confirmed after removal of anidulafungin pressure. The FKS1 gene was partially sequenced and a E671Q mutation was found. A computational approach suggests that it can play an important role in echinocandin resistance. Given the emerging importance of this mechanism for clinical resistance in pathogenic fungi, it would be prudent to be alert to the potential evolution of this resistant mechanism in Aspergillus spp infecting patients under echinocandins therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

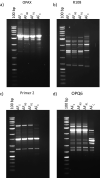
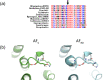
Similar articles
-
Stress-Induced Changes in the Lipid Microenvironment of β-(1,3)-d-Glucan Synthase Cause Clinically Important Echinocandin Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus.mBio. 2019 Jun 4;10(3):e00779-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00779-19. mBio. 2019. PMID: 31164462 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative in vivo dose-dependent activity of caspofungin and anidulafungin against echinocandin-susceptible and -resistant Aspergillus fumigatus.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011 Jun;66(6):1324-31. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr142. Epub 2011 Apr 11. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21486855
-
Emergence of Echinocandin Resistance Due to a Point Mutation in the fks1 Gene of Aspergillus fumigatus in a Patient with Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Nov 22;61(12):e01277-17. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01277-17. Print 2017 Dec. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28923871 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance in human pathogenic yeasts and filamentous fungi: prevalence, underlying molecular mechanisms and link to the use of antifungals in humans and the environment.Dan Med J. 2016 Oct;63(10):B5288. Dan Med J. 2016. PMID: 27697142 Review.
-
Acquired antifungal drug resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: epidemiology and detection.Med Mycol. 2011 Apr;49 Suppl 1:S90-5. doi: 10.3109/13693786.2010.508469. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Med Mycol. 2011. PMID: 20795765 Review.
Cited by
-
Azole Resistance and cyp51A Mutation of Aspergillus fumigatus in a Tertiary Referral Hospital in Taiwan.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Aug 26;8(9):908. doi: 10.3390/jof8090908. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135633 Free PMC article.
-
Caspofungin resistance in Candida albicans: genetic factors and synergistic compounds for combination therapies.Braz J Microbiol. 2022 Sep;53(3):1101-1113. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00739-9. Epub 2022 Mar 29. Braz J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35352319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Addressing Microbial Resistance Worldwide: Challenges over Controlling Life-Threatening Fungal Infections.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 10;12(2):293. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12020293. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36839565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug-Resistant Aspergillus spp.: A Literature Review of Its Resistance Mechanisms and Its Prevalence in Europe.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 31;12(11):1305. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111305. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developing novel antifungals: lessons from G protein-coupled receptors.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Mar;44(3):162-174. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2022.12.002. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36801017 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Desnos-Ollivier M, et al. Mutations in the fks1 gene in Candida albicans, C. tropicalis, and C. krusei correlate with elevated caspofungin MICs uncovered in AM3 medium using the method of the European Committee on Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008;52:3092–3098. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00088-08. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

