NRF2 is a key regulator of endothelial microRNA expression under proatherogenic stimuli
- PMID: 32683448
- PMCID: PMC8064437
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa219
NRF2 is a key regulator of endothelial microRNA expression under proatherogenic stimuli
Abstract
Aims: Oxidized phospholipids and microRNAs (miRNAs) are increasingly recognized to play a role in endothelial dysfunction driving atherosclerosis. NRF2 transcription factor is one of the key mediators of the effects of oxidized phospholipids, but the gene regulatory mechanisms underlying the process remain obscure. Here, we investigated the genome-wide effects of oxidized phospholipids on transcriptional gene regulation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells and aortic endothelial cells with a special focus on miRNAs.
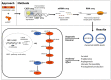
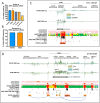
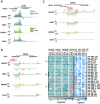
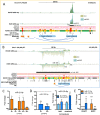
Methods and results: We integrated data from HiC, ChIP-seq, ATAC-seq, GRO-seq, miRNA-seq, and RNA-seq to provide deeper understanding of the transcriptional mechanisms driven by NRF2 in response to oxidized phospholipids. We demonstrate that presence of NRF2 motif and its binding is more prominent in the vicinity of up-regulated transcripts and transcriptional initiation represents the most likely mechanism of action. We further identified NRF2 as a novel regulator of over 100 endothelial pri-miRNAs. Among these, we characterize two hub miRNAs miR-21-5p and miR-100-5p and demonstrate their opposing roles on mTOR, VEGFA, HIF1A, and MYC expressions. Finally, we provide evidence that the levels of miR-21-5p and miR-100-5p in exosomes are increased upon senescence and exhibit a trend to correlate with the severity of coronary artery disease.
Conclusion: Altogether, our analysis provides an integrative view into the regulation of transcription and miRNA function that could mediate the proatherogenic effects of oxidized phospholipids in endothelial cells.
Keywords: miR-21-5p • miR-100-5p • NRF2 • Atherosclerosis.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures


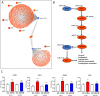
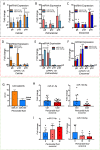
Comment in
-
NRF2: a key regulator of endothelial microRNA transcription.Cardiovasc Res. 2021 Apr 23;117(5):1241-1242. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvaa347. Cardiovasc Res. 2021. PMID: 33351890 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
NRF2 regulates endothelial glycolysis and proliferation with miR-93 and mediates the effects of oxidized phospholipids on endothelial activation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Feb 16;46(3):1124-1138. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1155. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29161413 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes-Mediated LncRNA ZEB1-AS1 Facilitates Cell Injuries by miR-590-5p/ETS1 Axis Through the TGF-β/Smad Pathway in Oxidized Low-density Lipoprotein-induced Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 1;77(4):480-490. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000000974. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33818551
-
MiR-135b-5p and MiR-499a-3p Promote Cell Proliferation and Migration in Atherosclerosis by Directly Targeting MEF2C.Sci Rep. 2015 Jul 17;5:12276. doi: 10.1038/srep12276. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26184978 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in endothelial senescence and atherosclerosis.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013 Dec;6(6):924-30. doi: 10.1007/s12265-013-9487-7. Epub 2013 Jun 29. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2013. PMID: 23812745 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals molecular characterization and immune landscape of PANoptosis-related genes in atherosclerosis.Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun;73(6):961-978. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01877-6. Epub 2024 Apr 8. Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38587531
-
MiR-144-5p and miR-21-5p do not drive bone disease in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes mellitus.JBMR Plus. 2024 Apr 6;8(5):ziae036. doi: 10.1093/jbmrpl/ziae036. eCollection 2024 May. JBMR Plus. 2024. PMID: 38606150 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of microRNA-512-3p enhances the viability and suppresses the apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells, alleviates autophagy and endoplasmic reticulum stress as well as represses atherosclerotic lesions in atherosclerosis by adjusting spliced/unspliced ratio of X-box binding protein 1 (XBP-1S/XBP-1U).Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(2):12469-12481. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2006862. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34783632 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Diet-Gut Microbiota-Epigenetics Crosstalk Relevant to Neonatal Diabetes.Genes (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;14(5):1017. doi: 10.3390/genes14051017. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37239377 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic characterization of seed overlap microRNA cotargeting associated with lupus pathogenesis.BMC Biol. 2022 Nov 11;20(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01447-4. BMC Biol. 2022. PMID: 36357926 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nazari-Jahantigh M, Egea V, Schober A, Weber C.. MicroRNA-specific regulatory mechanisms in atherosclerosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2015;89:35–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

