Survival outcomes and independent response assessment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: 42-month follow-up of a randomized phase 3 clinical trial
- PMID: 32661118
- PMCID: PMC7359377
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000891
Survival outcomes and independent response assessment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: 42-month follow-up of a randomized phase 3 clinical trial
Erratum in
-
Correction: Survival outcomes and independent response assessment with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: 42-month follow-up of a randomized phase 3 clinical trial.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 May;9(5):e000891corr1. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-000891corr1. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33941652 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: The extent to which response and survival benefits with immunotherapy-based regimens persist informs optimal first-line treatment options. We provide long-term follow-up in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC) receiving first-line nivolumab plus ipilimumab (NIVO+IPI) versus sunitinib (SUN) in the phase 3 CheckMate 214 trial. Survival, response, and safety outcomes with NIVO+IPI versus SUN were assessed after a minimum of 42 months of follow-up.
Methods: Patients with aRCC were enrolled from October 16, 2014, through February 23, 2016. Patients stratified by International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium (IMDC) risk and region were randomized to nivolumab (3 mg/kg) plus ipilimumab (1 mg/kg) every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab (3 mg/kg) every 2 weeks; or SUN (50 mg) once per day for 4 weeks (6-week cycle). Primary endpoints: overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and objective response rate (ORR) per independent radiology review committee in IMDC intermediate-risk/poor-risk patients. Secondary endpoints: OS, PFS, and ORR in the intention-to-treat (ITT) population and safety. Favorable-risk patient outcomes were exploratory.
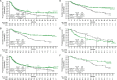
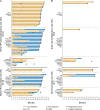
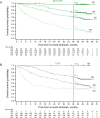
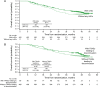
Results: Among ITT patients, 550 were randomized to NIVO+IPI (425 intermediate/poor risk; 125 favorable risk) and 546 to SUN (422 intermediate/poor risk; 124 favorable risk). Among intermediate-risk/poor-risk patients, OS (HR, 0.66; 95% CI, 0.55-0.80) and PFS (HR, 0.75; 95% CI, 0.62-0.90) benefits were observed, and ORR was higher (42.1% vs 26.3%) with NIVO+IPI versus SUN. In ITT patients, both OS benefits (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.61-0.86) and higher ORR (39.1% vs 32.6%) were observed with NIVO+IPI versus SUN. In favorable-risk patients, HR for death was 1.19 (95% CI, 0.77-1.85) and ORR was 28.8% with NIVO+IPI versus 54.0% with SUN. Duration of response was longer (HR, 0.46-0.54), and more patients achieved complete response (10.1%-12.8% vs 1.4%-5.6%) with NIVO+IPI versus SUN regardless of risk group. The incidence of treatment-related adverse events was consistent with previous reports.
Conclusions: NIVO+IPI led to improved efficacy outcomes versus SUN in both intermediate-risk/poor-risk and ITT patients that were maintained through 42 months' minimum follow-up. A complete response rate >10% was achieved with NIVO+IPI regardless of risk category, with no new safety signals detected in either arm. These results support NIVO+IPI as a first-line treatment option with the potential for durable response.
Trial registration number: NCT02231749.
Keywords: CTLA-4 antigen; clinical trials, phase III as topic; immunotherapy; kidney neoplasms; programmed cell death 1 receptor.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. RJM reports consulting or advisory roles with Eisai, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Incyte, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer, and research funding/travel/accommodations/expenses from Bristol-Myers Squibb Company (BMS), Eisai, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, and Pfizer. BE reports honoraria, consulting, or advisory roles with BMS, EUSA Pharma, Ipsen, Novartis, Pfizer, and Roche. DFM reports consulting or advisory roles with Array BioPharma, BMS, Exelixis, Genentech/Roche, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer, and research finding from BMS (Inst), Genetech/Roche (Inst), Merck (Inst), Novartis (Inst), and Prometheus (Inst). OAF reports employment, stock or other ownership, and honoraria from Pfizer (I); consulting or advisory roles with BMS Chile and BMS Colombia; and travel, accommodations, expenses from Roche and Tecnofarma. BM reports honoraria from and advisory roles with Bayer, MSD, Merck Serono, Sanofi, Servie, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Janssen, Eisai, and Eli Lilly, and travel expenses from Merck Serono. TP reports honoraria from Merck, BMS, Pfizer, Roche, Ipsen, Novartis, Exelixis, and AstraZeneca, and research funding from AstraZeneca (Inst), Roche (Inst), and Novartis (Inst). FD reports research funding from Ipsen (Inst), Novartis (Inst), and Pfizer (Inst). ERP reports consulting or advisory roles with BMS, Genentech/Roche, Merck, Clovis, Exelixis, Seattle Genetics, Incyte, Janssen, and Flatiron Health; research funding from Astellas Pharma (Inst), AstraZeneca (Inst) BMS (Inst), Genentech/Roche (Inst), Merck (Inst), Peloton (Inst), and Pfizer (Inst); patents, royalties, and other intellectual property: US Patent Application No 14/588,503, pending, filed January 2, 2015; and the following other relationships: BMS (fees for development of educational presentations); Merck (fees for development of educational presentations); Roche (fees for development of educational presentations); Novartis (fees for development of educational presentations), and Exelixis (personal fees). PB reports consulting or advisory roles with BMS, Pfizer, MSD Oncology, Novartis, Ipsen, Roche, Janssen Cilag, and EUSA Pharma, and honoraria from Astellas Pharma and Amgen. HJH reports consulting or advisory roles with BMS, Pfizer, Exelixis, Merck, Corvus, Surface Oncology, Armo Biosciences, and Novartis, and research funding from BMS and Merck. SG reports consulting or advisory roles with Astellas, BMS, Novartis, Bayer, Pfizer, Exelixis, AstraZeneca, Janssen Oncology, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Genentech/Roche, EMD Serono, and Sanofi, and research funding from Pfizer (Inst), Acceleron Pharma (Inst), Merck (Inst), Agensys (Inst), Novartis (Inst), BMS (Inst), Bayer (Inst), Eisai (Inst), and Corvus (Inst). VG reports consulting or advisory roles with BMS, Pfizer, Novartis, Lilly, MSD Oncology, Ipsen, Janssen Cilag, and Onkowissen; consulting or advisory roles with Bayer, BMS, Pfizer, Ipsen, and AstraZeneca; stock or other ownership in MSD, BMS, and AstraZeneca; honoraria from BMS, Pfizer, Novartis, Ipsen, Eisai, Bayer, MSD Oncology, Merck Serono, Roche, Lilly, PharmaMar, AstraZeneca, EUSA Pharma, Janssen Cilag, Asklepios Clinics, Diakonie Clinic, Dortmund Hospital, and Clinic of Oldenburg; and research funding from Novartis (Inst). CP reports consulting or advisory roles with BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Ipsen, EUSA, Eisai, and General Electric; speakers’ bureau fees from BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Ipsen EUSA, Eisai, General Electric, Janssen, and AstraZeneca; research funding from Pfizer (Inst); expert testimony fees from Pfizer and EUSA; and travel, accommodations, and expenses from Roche. VN reports honoraria from MSD and TEVA. AR reports consulting or advisory roles with Pfizer, BMS, Roche, Ipsen, Merck, and AstraZeneca; research funding from Pfizer (Inst); and non-financial support from Pfizer, BMS, Ipsen, Merck, MSD, and AstraZeneca. TKC reports research (Institutional and personal) funding from AstraZeneca, Alexion, Bayer, BMS/ER Squibb and sons LLC, Cerulean, Eisai, Foundation Medicine Inc, Exelixis, Ipsen, Tracon, Genentech, Roche, Roche Products Limited, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Peloton, Pfizer, Prometheus Labs, Corvus, Calithera, Analysis Group, Sanofi/Aventis, and Takeda; honoraria from AstraZeneca, Alexion, Sanofi/Aventis, Bayer, BMS/ER Squibb and sons LLC, Cerulean, Eisai, Foundation Medicine Inc, Exelixis, Genentech, Roche, Roche Products Limited, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novartis, Peloton, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Prometheus Labs, Corvus, Ipsen, UptoDate, Analysis Group, NCCN, Michael J Hennessy (MJH) Associates, Inc (Healthcare Communications Company with several brands such as OnClive, PeerView and PER), L-path, Kidney Cancer Journal, Clinical Care Options, Platform Q, Navinata Healthcare, Harborside Press, American Society of Medical Oncology, New England Journal of Medicine, Lancet Oncology, Heron Therapeutics, and Lilly; consulting or advisory roles with AstraZeneca, Alexion, Sanofi/Aventis, Bayer, BMS/ER Squibb and Sons LLC, Cerulean, Eisai, Foundation Medicine Inc, Exelixis, Genentech, Heron Therapeutics, Lilly, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novartis, Peloton, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Prometheus Labs, Corvus, Ipsen, UptoDate, NCCN, and Analysis Group; and the following patents, royalties or other intellectual properties: International Patent Application No PCT/US2018/12209, entitled 'PBRM1 Biomarkers Predictive of Anti-Immune Checkpoint Response', filed January 3, 2018, claiming priority to US Provisional Patent Application No 62/445,094, filed January 11, 2017, International Patent Application No PCT/US2018/058430, entitled 'Biomarkers of Clinical Response and Benefit to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy', filed October 31, 2018, claiming priority to US Provisional Patent Application No 62/581,175, filed November 3, 2017. BIR reports research funding from BMS, Pfizer, Merck, GNE, Roche, Aveo, and AstraZeneca; consulting or advisory roles with BMS, Pfizer, GNE/Roche, Aveo, Novartis, Synthorx, Peloton, Compugen, Merck, Arravive, Surface Oncology, and 3D Medicines, and stock or other ownership in PTC Therapeutics. CKK reports honoraria from BMS, Pfizer, Ipsen, and Eisai; and consulting or advisory roles with BMS, Pfizer, Ipsen, Eisai, Roche, Astellas, and Janssen. SST reports consulting or advisory roles with BMS, Calithera Biosciences, and Prometheus Laboratories; and research funding from BMS (Inst), Calithera Biosciences (Inst), Merck (Inst), Nektar Therapeutics (Inst), Peloton Therapeutics (Inst), Jounce Therapeutics (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), Genentech (Inst), Prometheus Laboratories (Inst), ARGOS Therapeutics (Inst), and Clinigen (Inst). M-OG reports lecture or advisory roles with Novartis, BMS, Pfizer, Bayer, Astellas, Intuitive Surgical, Hexal, Apogepha, AstraZeneca, MSD Janssen Cilag, ONO Pharmaceuticals, Ipsen, Medac Merck, and Serono; and research funding from Novartis, BMS, and Intuitive Surgical. HG reports consulting or advisory roles with Astellas, BMS, Novartis, Pfizer, MSD, AstraZeneca, Ipsen, and Roche. RL-A reports personal fees from BMS, MSD, and Pfizer. PFG reports research funding from BMS, Pfizer, Merck, MSD, and Roche. AA reports research funding from BMS, Pfizer, Merck, and Exelixis, and speakers’ bureau fees from Pfizer, Exelixis, BMS, and Merck. YT reports honoraria from Pfizer, Novartis, ONO Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Astellas, BMS, and Chugai; consulting or advisory roles with ONO Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd, Novartis, and Taiho; and research funding from Takeda (Inst), Pfizer (Inst), ONO Pharmaceutical Co, Ltd (Inst), Astellas (Inst), Novartis (Inst), and Chugai (Inst). MBM reports employment with and stock or other ownership in BMS. SSS reports employment with and stock or other ownership in BMS. NMT reports research funding from BMS, Calithera Biosciences, Nektar Therapeutics, Exelixis, Pfizer, Novartis, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, Mirati Therapeutics, Takeda, Epizyme, and Eisai Medical Research; consulting, advisory, travel accommodations and expenses from BMS, Calithera Biosciences, Nektar Therapeutics, Exelixis, Pfizer, Novartis, Eisai Medical Research, Ipsen, Lilly Oncology, Neoleukin Therapeutics, Surface Oncology, ONO Pharmaceutical, and Oncorena; and honoraria from BMS, Exelixis, Nektar Therapeutics, Calithera Biosciences, Eisai Medical Research, ONO Pharmaceutical, Eli Lilly, Oncorena, Ipsen, and Surface Oncology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in previously untreated advanced renal-cell carcinoma: analysis of Japanese patients in CheckMate 214 with extended follow-up.Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jan 24;50(1):12-19. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyz132. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31633185 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib for first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended 8-year follow-up results of efficacy and safety from the phase III CheckMate 214 trial.Ann Oncol. 2024 Nov;35(11):1026-1038. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2024.07.727. Epub 2024 Aug 2. Ann Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39098455 Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term outcomes with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib in first-line treatment of patients with advanced sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2022 Dec;10(12):e005445. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005445. J Immunother Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36549781 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risks and benefits of reinduction ipilimumab/nivolumab in melanoma patients previously treated with ipilimumab/nivolumab.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Oct;9(10):e003395. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-003395. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34702752 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and Safety of First-line Systemic Therapy for Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis.Eur Urol Open Sci. 2022 Jan 22;37:14-26. doi: 10.1016/j.euros.2021.12.007. eCollection 2022 Mar. Eur Urol Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 35128482 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Iron accumulation typifies renal cell carcinoma tumorigenesis but abates with pathological progression, sarcomatoid dedifferentiation, and metastasis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 5;12:923043. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.923043. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992801 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment-free survival and partitioned survival analysis of patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus sunitinib: 5-year update of CheckMate 214.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Jul 25;12(7):e009495. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-009495. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39060019 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab versus Sunitinib in First-line Treatment of Patients with Advanced Sarcomatoid Renal Cell Carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;27(1):78-86. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2063. Epub 2020 Sep 1. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 32873572 Free PMC article.
-
Frontier knowledge and future directions of programmed cell death in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Mar 5;10(1):113. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01880-0. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38443363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Pathological Complete Response to the Combination of Ipilimumab and Nivolumab in a Patient with Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Feb 23;58(3):336. doi: 10.3390/medicina58030336. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35334512 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
