M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promote gastric cancer progression via a microRNA-130b-3p/MLL3/GRHL2 signaling cascade
- PMID: 32660626
- PMCID: PMC7359233
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-020-01626-7
M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promote gastric cancer progression via a microRNA-130b-3p/MLL3/GRHL2 signaling cascade
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles promote gastric cancer progression via a microRNA-130b-3p/MLL3/GRHL2 signaling cascade.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jan 24;42(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02604-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36691042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
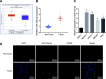
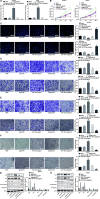
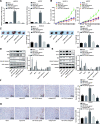
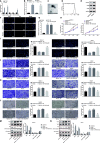
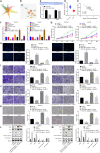
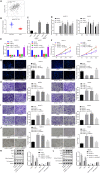
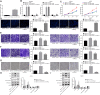
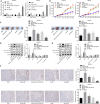
Background: Transfer of noncoding microRNAs (miRNAs) by extracellular vesicles (EVs) promotes the development of chemoresistance in many tumor types. Additionally, restoration or depletion of several miRNAs has been observed in multiple cancer types including gastric cancer (GC). In this present study, we aimed to investigate the mechanism of miR-130b-3p in M2 macrophage-derived EVs in the development of GC through regulation of mixed lineage leukemia 3 (MLL3) and grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2).
Methods: Expression of miR-130b-3p and GRHL2 was quantified in 63 pairs of cancerous and noncancerous gastric tissues. The predicted binding between miR-130b-3p and MLL3, together with the enrichment of MLL3, H3K4me1, and H3K27ac in gene enhancer region, was verified by luciferase activity assay and chromatin immunoprecipitation. Effects of miR-130b-3p on GC cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion, as well as tube formation of human umbilical endothelial vein cells (HUEVCs) were further determined by gain- and loss-of function assays in vitro.
Results: miR-130b-3p was upregulated in GC tissues, and miR-130b-3p promoted survival, metastasis and angiogenesis of GC cells as well as enhanced tumor formation and angiogenesis in GC in vivo. Additionally, miR-130b-3p delivered in M2 macrophage-derived EVs promoted survival, migration, invasion, and angiogenesis of GC cells. Notably, MLL3 inhibited GC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and vessel-like tube formation of HUEVCs by increasing GRHL2. Furthermore, downregulation of miR-130b-3p in M2 macrophage-derived EVs or upregulation of GRHL2 inhibited tumor formation and angiogenesis in GC.
Conclusion: This study highlights that EVs loaded with the specific miRNA cargo miR-130b-3p mediate communication between M2 macrophages and cancer cells in the tumor microenvironment through the modulation of MLL3 and GRHL2 in GC.
Keywords: Extracellular vesicles; GRHL2; Gastric cancer; M2 macrophages; MLL3; microRNA-130b-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of linc00152 inhibits the progression of gastric cancer by regulating microRNA-193b-3p/ETS1 axis.Cancer Biol Ther. 2019;20(4):461-473. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1529124. Epub 2018 Nov 7. Cancer Biol Ther. 2019. PMID: 30404587 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived extracellular vesicles containing microRNA-1290 promote immune escape of cancer cells through the Grhl2/ZEB1/PD-L1 axis in gastric cancer.Transl Res. 2021 May;231:102-112. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.12.003. Epub 2020 Dec 13. Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 33321257
-
TEAD4 modulated LncRNA MNX1-AS1 contributes to gastric cancer progression partly through suppressing BTG2 and activating BCL2.Mol Cancer. 2020 Jan 10;19(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1104-1. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 31924214 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in the gastric cancer tumor microenvironment.Mol Cancer. 2024 Aug 20;23(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-02084-x. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39164671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs in Diagnostics of Gastric Cancer.Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024 Jul;89(7):1211-1238. doi: 10.1134/S0006297924070058. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2024. PMID: 39218020 Review.
Cited by
-
Chromatin and noncoding RNA-mediated mechanisms of gastric tumorigenesis.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Jan;55(1):22-31. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00926-0. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36653445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering Macrophages via Nanotechnology and Genetic Manipulation for Cancer Therapy.Front Oncol. 2022 Jan 6;11:786913. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.786913. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35070992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A positive feedback loop between gastric cancer cells and tumor-associated macrophage induces malignancy progression.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 May 14;41(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02366-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35562774 Free PMC article.
-
M2 macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles facilitate CD8+T cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma via the miR-21-5p/YOD1/YAP/β-catenin pathway.Cell Death Discov. 2021 Jul 16;7(1):182. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00556-3. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34282135 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Metastasis and the Tumour Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 4;22(9):4859. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094859. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064331 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang XY, Zhang PY. Gastric cancer: somatic genetics as a guide to therapy. J Med Genet. 2017;54(5):305–312. - PubMed
-
- Li R, Liu B, Gao J. The application of nanoparticles in diagnosis and theranostics of gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;386:123–130. - PubMed
-
- Kawakami H, Okamoto I. Met-targeted therapy for gastric cancer: the importance of a biomarker-based strategy. Gastric Cancer. 2016;19(3):687–695. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

