Structural Basis for the Selective Inhibition of HDAC10, the Cytosolic Polyamine Deacetylase
- PMID: 32659072
- PMCID: PMC7442746
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00362
Structural Basis for the Selective Inhibition of HDAC10, the Cytosolic Polyamine Deacetylase
Abstract
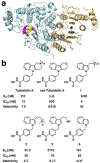
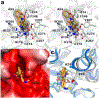
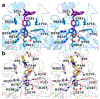
The cytosolic class IIb histone deacetylase HDAC10 is an emerging target for drug design. As an inducer of autophagy, its selective inhibition suppresses the autophagic response that otherwise attenuates the efficacy of cytotoxic cancer chemotherapy drugs. HDAC10 is a zinc-dependent polyamine deacetylase exhibiting maximal catalytic activity against N8-acetylspermidine. As revealed in the structure of Danio rerio (zebrafish) HDAC10, two conserved structural motifs direct this narrow substrate specificity: a 310 helix containing the P(E,A)CE motif that sterically constricts the active site and an electrostatic "gatekeeper," E274, that confers selectivity for cationic polyamine substrates. To accelerate drug design efforts targeting human HDAC10, we now report the preparation of "humanized" zebrafish HDAC10 in which two amino acid substitutions, A24E and D94A, yield an active site contour more similar to that of human HDAC10. X-ray crystal structures of this HDAC10 variant complexed with Tubastatin A and indole analogues bearing pendant tertiary amines reveal that inhibitors capable of hydrogen bonding with gatekeeper E274 exhibit high affinity and selectivity for HDAC10 over HDAC6 (the other class IIb isozyme). Moreover, these structures reveal that the P(E,A)CE motif helix can shift by up to 2 Å to accommodate the binding of bulky inhibitors. Thus, slender polyamine-like inhibitor structures are not exclusively required for selective, high affinity binding to HDAC10. Indeed, the flexibility of the P(E,A)CE motif helix could conceivably enable the binding of certain protein substrates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
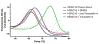
Similar articles
-
Design, Synthesis, and Structural Evaluation of Acetylated Phenylthioketone Inhibitors of HDAC10.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 Sep 5;15(10):1715-1723. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00293. eCollection 2024 Oct 10. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 39411528
-
Binding of N8-Acetylspermidine Analogues to Histone Deacetylase 10 Reveals Molecular Strategies for Blocking Polyamine Deacetylation.Biochemistry. 2019 Dec 10;58(49):4957-4969. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00906. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31746596 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamine Deacetylase Structure and Catalysis: Prokaryotic Acetylpolyamine Amidohydrolase and Eukaryotic HDAC10.Biochemistry. 2018 Jun 5;57(22):3105-3114. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00079. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29533602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Versatility in Catalysis and Inhibition of the Class IIb Histone Deacetylases.Acc Chem Res. 2024 Apr 16;57(8):1135-1148. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.3c00801. Epub 2024 Mar 26. Acc Chem Res. 2024. PMID: 38530703 Review.
-
X-ray Crystallographic Snapshots of Substrate Binding in the Active Site of Histone Deacetylase 10.Biochemistry. 2021 Feb 2;60(4):303-313. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00936. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Biochemistry. 2021. PMID: 33449614 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of histone deacetylase 10 (HDAC10) inhibitors that modulate autophagy in transformed cells.Eur J Med Chem. 2022 Apr 15;234:114272. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114272. Epub 2022 Mar 11. Eur J Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35306288 Free PMC article.
-
First Fluorescent Acetylspermidine Deacetylation Assay for HDAC10 Identifies Selective Inhibitors with Cellular Target Engagement.Chembiochem. 2022 Jul 19;23(14):e202200180. doi: 10.1002/cbic.202200180. Epub 2022 Jun 10. Chembiochem. 2022. PMID: 35608330 Free PMC article.
-
Distribution and diversity of classical deacylases in bacteria.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 3;15(1):9496. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53903-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39489725 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and Structural Evaluation of Acetylated Phenylthioketone Inhibitors of HDAC10.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 Sep 5;15(10):1715-1723. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00293. eCollection 2024 Oct 10. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 39411528
-
Aza-SAHA Derivatives Are Selective Histone Deacetylase 10 Chemical Probes That Inhibit Polyamine Deacetylation and Phenocopy HDAC10 Knockout.J Am Chem Soc. 2022 Oct 19;144(41):18861-18875. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c05030. Epub 2022 Oct 6. J Am Chem Soc. 2022. PMID: 36200994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gregoretti IV, Lee YM, and Goodson HV (2004) Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: functional implication of phylogenetic analysis. J. Mol. Biol 338, 17–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

