Cell-type-specific differences in KDEL receptor clustering in mammalian cells
- PMID: 32645101
- PMCID: PMC7347126
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235864
Cell-type-specific differences in KDEL receptor clustering in mammalian cells
Abstract
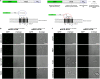
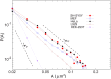
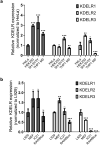
In eukaryotic cells, KDEL receptors (KDELRs) facilitate the retrieval of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) luminal proteins from the Golgi compartment back to the ER. Apart from the well-documented retention function, recent findings reveal that the cellular KDELRs have more complex roles, e.g. in cell signalling, protein secretion, cell adhesion and tumorigenesis. Furthermore, several studies suggest that a sub-population of KDELRs is located at the cell surface, where they could form and internalize KDELR/cargo clusters after K/HDEL-ligand binding. However, so far it has been unclear whether there are species- or cell-type-specific differences in KDELR clustering. By comparing ligand-induced KDELR clustering in different mouse and human cell lines via live cell imaging, we show that macrophage cell lines from both species do not develop any clusters. Using RT-qPCR experiments and numerical analysis, we address the role of KDELR expression as well as endocytosis and exocytosis rates on the receptor clustering at the plasma membrane and discuss how the efficiency of directed transport to preferred docking sites on the membrane influences the exponent of the power-law distribution of the cluster size.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
KDEL Receptors: Pathophysiological Functions, Therapeutic Options, and Biotechnological Opportunities.Biomedicines. 2022 May 25;10(6):1234. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061234. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cargo binding promotes KDEL receptor clustering at the mammalian cell surface.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 29;6:28940. doi: 10.1038/srep28940. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27353000 Free PMC article.
-
KDEL Receptor 1 Contributes to Cell Surface Association of Protein Disulfide Isomerases.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(4):850-868. doi: 10.33594/000000059. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30958660
-
A Golgi-based KDELR-dependent signalling pathway controls extracellular matrix degradation.Oncotarget. 2015 Feb 20;6(5):3375-93. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3270. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25682866 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenic Effects of Impaired Retrieval between the Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Complex.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 9;20(22):5614. doi: 10.3390/ijms20225614. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31717602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Engineering a Rapid Insulin Release System Controlled By Oral Drug Administration.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Mar;9(9):e2105619. doi: 10.1002/advs.202105619. Epub 2022 Jan 20. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35048556 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between KDEL receptor and EGF receptor mediates cell proliferation and migration via STAT3 signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 20;22(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01517-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38378560 Free PMC article.
-
KDEL Receptors: Pathophysiological Functions, Therapeutic Options, and Biotechnological Opportunities.Biomedicines. 2022 May 25;10(6):1234. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061234. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the potential biological significance of KDELR family genes in lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 27;14(1):14820. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65425-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38937522 Free PMC article.
-
KDEL Receptor Trafficking to the Plasma Membrane Is Regulated by ACBD3 and Rab4A-GTP.Cells. 2023 Apr 4;12(7):1079. doi: 10.3390/cells12071079. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson DW, Lewis MJ and Pelham HR. pH-dependent binding of KDEL to its receptor in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1993; 268:7465–7468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

