Protein acetylation derepresses Serotonin Synthesis to potentiate Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function through HDAC1-PKA-Tph1 signaling
- PMID: 32641996
- PMCID: PMC7330849
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.44459
Protein acetylation derepresses Serotonin Synthesis to potentiate Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function through HDAC1-PKA-Tph1 signaling
Abstract
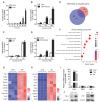
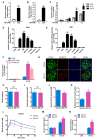
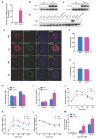
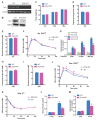
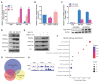
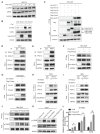
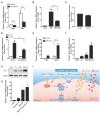
Rationale: Protein acetylation is tightly linked to transcriptional control and energy metabolism. However, the role of protein acetylation in islet function remains enigmatic. This study aims to determine how protein acetylation controls β-cell function and explore the underlying mechanism. Methods: The gene-expression profiles were analyzed for rat islets in response to two histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. Insulin secretion, tryptophan hydroxylase 1 (Tph1) expression, and serotonin synthesis of rat islets were detected after HDAC inhibitor treatment both in vivo and ex vivo. β-cell-specific Tph1-overexpressing transgenic rats and β-cell-specific Tph1 knockout mice were constructed to evaluate the role of Tph1 in β-cell function. The deacetylation of PKA in β-cells by HDAC1 was investigated by adenoviral infection, immunoprecipitation, and western blot. Results: Inhibition of HDACs greatly potentiated pancreatic β-cell function and reprogrammed transcriptional landscape of islets. Among the commonly up-regulated genes by two pan-HDAC inhibitors, Tph1 displayed the most prominent change. Specifically, inhibition of HDAC1 and HDAC3 by MS-275 strongly promoted Tph1 expression and endogenous serotonin synthesis in rat islets, concomitantly with enhanced insulin secretory capacity in vivo and ex vivo. β-cell-specific Tph1-overexpressing transgenic rats exhibited improved glucose tolerance and amplified glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. On the contrary, β-cell-specific Tph1 knockout mice displayed glucose intolerance and impaired insulin secretion with aging. Moreover, depletion of Tph1 in β-cells abrogated MS-275-induced insulin hypersecretion. Overexpression of HDAC1, not HDAC3, inhibited Tph1 transcriptional activity and decreased MS-275-stimulated Tph1 expression. Mechanistically, HDAC1 deacetylated PKA catalytic subunit and decreased its activity, resulting in Tph1 transcriptional repression. The acetylation mimetic K62Q mutant of PKA increased its catalytic activity. HDAC1 inhibition exerted a synergistic effect with cAMP/PKA signal on Tph1 expression. Conclusions: The present findings highlight a novel role of HDAC1-PKA-Tph1 signaling in governing β-cell functional compensation by derepressing serotonin synthesis.
Keywords: Beta-cell function; HDAC1; PKA; Protein acetylation; Serotonin; Tph1.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glucose potentiates β-cell function by inducing Tph1 expression in rat islets.FASEB J. 2017 Dec;31(12):5342-5355. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700351R. Epub 2017 Aug 9. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28794173
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition by MS-275 potentiates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion without affecting glucose oxidation.Life Sci. 2020 Sep 15;257:118073. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118073. Epub 2020 Jul 11. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32663574
-
Functional role of serotonin in insulin secretion in a diet-induced insulin-resistant state.Endocrinology. 2015 Feb;156(2):444-52. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1687. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25426873 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylases 1 and 3 but not 2 mediate cytokine-induced beta cell apoptosis in INS-1 cells and dispersed primary islets from rats and are differentially regulated in the islets of type 1 diabetic children.Diabetologia. 2012 Sep;55(9):2421-31. doi: 10.1007/s00125-012-2615-0. Epub 2012 Jul 7. Diabetologia. 2012. PMID: 22772764
-
Role of HDAC inhibitors in diabetes mellitus.Curr Res Transl Med. 2020 Apr;68(2):45-50. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 31477543 Review.
Cited by
-
Activated Platelets Autocrine 5-Hydroxytryptophan Aggravates Sepsis-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Promoting Neutrophils Extracellular Traps Formation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 17;9:777989. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.777989. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35111753 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Pancreas Development and Function.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2024;239:1-30. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-62232-8_1. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39283480 Review.
-
Exploring histone deacetylases in type 2 diabetes mellitus: pathophysiological insights and therapeutic avenues.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Jun 11;16(1):78. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01692-0. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38862980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
THADA inhibition in mice protects against type 2 diabetes mellitus by improving pancreatic β-cell function and preserving β-cell mass.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 23;14(1):1020. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36680-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36823211 Free PMC article.
-
Light-gated Integrator for Highlighting Kinase Activity in Living Cells.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 20:2024.03.18.585554. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.18.585554. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 6;15(1):7804. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51270-4. PMID: 38562887 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Prentki M, Matschinsky FM, Madiraju SR. Metabolic signaling in fuel-induced insulin secretion. Cell Metab. 2013;18:162–85. - PubMed
-
- Menzies KJ, Zhang H, Katsyuba E, Auwerx J. Protein acetylation in metabolism - metabolites and cofactors. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2016;12:43–60. - PubMed
-
- Gallinari P, Di Marco S, Jones P, Pallaoro M, Steinkuhler C. HDACs, histone deacetylation and gene transcription: from molecular biology to cancer therapeutics. Cell Res. 2007;17:195–211. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

