Matrine inhibits the growth of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cells by modulating CaMKIIγ-c-Myc signaling pathway
- PMID: 32641029
- PMCID: PMC7346655
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-020-03006-2
Matrine inhibits the growth of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cells by modulating CaMKIIγ-c-Myc signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: C-Myc overexpression is associated with poor prognosis and aggressive progression of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (NKTCL). Matrine, a main alkaloid of the traditional Chinese herb Sophora flavescens Ait, has been shown to inhibit cellular proliferation and induce apoptosis of various cancer cells. The present study investigated the effects and possible mechanisms of matrine inhibiting the growth of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cells.
Methods: The effects of matrine on the proliferation, apoptosis and expression of apoptotic molecules, STAT3, LMP1, RUNX3, EZH2 and activation of CaMKIIγ/c-Myc pathway were examined in cultured NKTCL cell line NK92 cells.
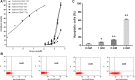
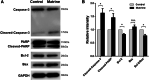
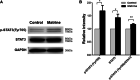
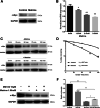
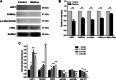
Results: In cultured NK92 cells, matrine inhibited the proliferation in a dose and time dependent manner. The IC50 value of matrine was 1.71 mM for 72 h post exposure in NK92 cells. Matrine induced apoptosis with decreased Bcl-2 expression and the proteasome-dependent degradation of c-Myc protein in NK92 cells. c-Myc protein half-life in NK92 was reduced from 80.7 min to 33.4 min after matrine treatment, which meant the stability of c-Myc was decreased after matrine exposure. Furthermore, we found that matrine downregulated c-Myc phosphorylation at Ser62 together with the inhibition of CaMKIIγ, a key regulator of c-Myc protein in NKTCL. The downregulation of c-Myc transcription by matrine was mediated through LMP1 inhibition. We also observed that anti-proliferative activity of matrine was irrelevant to STAT3, RUNX3 and EZH2.
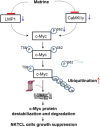
Conclusions: The results of the present study indicated that matrine inhibits the growth of natural killer/T-cell lymphoma cells by modulating LMP1-c-Myc and CaMKIIγ-c-Myc signaling pathway.
Keywords: C-Myc; CaMKIIγ; LMP1; Matrine; NK/T-cell lymphoma; NK92 cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrine suppresses cell growth of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma via inhibiting CaMKIIγ/c-Myc/CDK6 signaling pathway.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jun 4;21(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03315-0. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34088288 Free PMC article.
-
Matrine suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in human cholangiocarcinoma cells through suppression of JAK2/STAT3 signaling.Pharmacol Rep. 2015 Apr;67(2):388-93. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2014.10.016. Epub 2014 Nov 5. Pharmacol Rep. 2015. PMID: 25712669
-
Matrine induces apoptosis of human multiple myeloma cells via activation of the mitochondrial pathway.Leuk Lymphoma. 2010 Jul;51(7):1337-46. doi: 10.3109/10428194.2010.488708. Leuk Lymphoma. 2010. PMID: 20528251
-
Structural Modifications of Matrine-Type Alkaloids.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(9):730-744. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666161104150334. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 27823557 Review.
-
Matrine-Family Alkaloids: Versatile Precursors for Bioactive Modifications.Med Chem. 2020;16(4):431-453. doi: 10.2174/1573406415666190507121744. Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31378199 Review.
Cited by
-
Quinolizidine-Type Alkaloids: Chemodiversity, Occurrence, and Bioactivity.ACS Omega. 2023 Jul 28;8(31):27862-27893. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c02179. eCollection 2023 Aug 8. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37576649 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrine, a potential c-Myc inhibitor, suppresses ribosome biogenesis and nucleotide metabolism in myeloid leukemia.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 21;13:1027441. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1027441. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339620 Free PMC article.
-
Remodeling tumor microenvironment with natural products to overcome drug resistance.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1051998. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1051998. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Machine Learning Algorithms Identify Target Genes and the Molecular Mechanism of Matrine against Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(6):847-859. doi: 10.2174/1573409920666230821102806. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37605410
-
The mechanism of TGF-β mediating BRD4/STAT3 signaling pathway to promote fibroblast proliferation and thus promote keloid progression.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 21;10(19):e38188. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38188. eCollection 2024 Oct 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39391472 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Qi SN, Xu LM, Yuan ZY, Wu T, Zhu SY, Shi M, Su H, Wang Y, He X, Zhang LL, Wu G, Qu BL, Qian LT, Hou XR, Zhang FQ, Zhang YJ. Effect of primary tumor invasion on treatment and survival in extranodal nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma in the modern chemotherapy era: a multicenter study from the China lymphoma collaborative group (CLCG). Leuk Lymphoma. 2019. 10.1080/10428194.2019.1602265. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

