miR-7 Regulates GLP-1-Mediated Insulin Release by Targeting β-Arrestin 1
- PMID: 32640511
- PMCID: PMC7407368
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9071621
miR-7 Regulates GLP-1-Mediated Insulin Release by Targeting β-Arrestin 1
Abstract
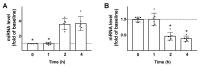
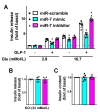
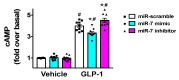
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) has been shown to potentiate glucose-stimulated insulin secretion binding GLP-1 receptor on pancreatic β cells. β-arrestin 1 (βARR1) is known to regulate the desensitization of GLP-1 receptor. Mounting evidence indicates that microRNAs (miRNAs, miRs) are fundamental in the regulation of β cell function and insulin release. However, the regulation of GLP-1/βARR1 pathways by miRs has never been explored. Our hypothesis is that specific miRs can modulate the GLP-1/βARR1 axis in β cells. To test this hypothesis, we applied a bioinformatic approach to detect miRs that could target βARR1; we identified hsa-miR-7-5p (miR-7) and we validated the specific interaction of this miR with βARR1. Then, we verified that GLP-1 was indeed able to regulate the transcription of miR-7 and βARR1, and that miR-7 significantly regulated GLP-1-induced insulin release and cyclic AMP (cAMP) production in β cells. Taken together, our findings indicate, for the first time, that miR-7 plays a functional role in the regulation of GLP-1-mediated insulin release by targeting βARR1. These results have a decisive clinical impact given the importance of drugs modulating GLP-1 signaling in the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: cAMP; diabetes; epigenetics; glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS); miRNA-7; β-arrestin 1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Beta-Arrestin-1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 signaling to insulin secretion in cultured pancreatic beta cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 May 6;105(18):6614-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710402105. Epub 2008 Apr 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18445652 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of miR-132 and miR-212 Expression by Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 (GLP-1) in Rodent and Human Pancreatic β-Cells.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Sep;29(9):1243-53. doi: 10.1210/me.2014-1335. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26218441 Free PMC article.
-
GLP-1 and GIP receptors signal through distinct β-arrestin 2-dependent pathways to regulate pancreatic β cell function.Cell Rep. 2023 Nov 28;42(11):113326. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113326. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37897727
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1-potentiated insulin secretion and proliferation of pancreatic β-cells.J Diabetes. 2014 Sep;6(5):394-402. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12161. Epub 2014 May 22. J Diabetes. 2014. PMID: 24725840 Review.
-
Anti-diabetic actions of glucagon-like peptide-1 on pancreatic beta-cells.Metabolism. 2014 Jan;63(1):9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.09.010. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Metabolism. 2014. PMID: 24140094 Review.
Cited by
-
A Retinoic Acid Receptor β 2 Agonist Improves Cardiac Function in a Heart Failure Model.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021 Nov;379(2):182-190. doi: 10.1124/jpet.121.000806. Epub 2021 Aug 13. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021. PMID: 34389654 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Endothelial G Protein-Coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Angioedema.Hypertension. 2020 Nov;76(5):1625-1636. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15130. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32895019 Free PMC article.
-
miR-142 Targets TIM-1 in Human Endothelial Cells: Potential Implications for Stroke, COVID-19, Zika, Ebola, Dengue, and Other Viral Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 6;23(18):10242. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810242. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142146 Free PMC article.
-
miR-24 Targets the Transmembrane Glycoprotein Neuropilin-1 in Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells.Noncoding RNA. 2021 Feb 2;7(1):9. doi: 10.3390/ncrna7010009. Noncoding RNA. 2021. PMID: 33540664 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-7 in Cancer Development.Biomedicines. 2021 Mar 23;9(3):325. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9030325. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33806891 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

