Merkel cell polyomavirus small tumour antigen activates the p38 MAPK pathway to enhance cellular motility
- PMID: 32639530
- PMCID: PMC7398664
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20200399
Merkel cell polyomavirus small tumour antigen activates the p38 MAPK pathway to enhance cellular motility
Abstract
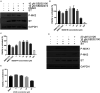
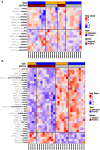
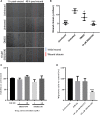
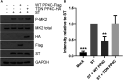
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive skin cancer with high rates of recurrence and metastasis. Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV) is associated with the majority of MCC cases. MCPyV-induced tumourigenesis is largely dependent on the expression of the small tumour antigen (ST). Recent findings implicate MCPyV ST expression in the highly metastatic nature of MCC by promoting cell motility and migration, through differential expression of cellular proteins that lead to microtubule destabilisation, filopodium formation and breakdown of cell-cell junctions. However, the molecular mechanisms which dysregulate these cellular processes are yet to be fully elucidated. Here, we demonstrate that MCPyV ST expression activates p38 MAPK signalling to drive cell migration and motility. Notably, MCPyV ST-mediated p38 MAPK signalling occurs through MKK4, as opposed to the canonical MKK3/6 signalling pathway. In addition, our results indicate that an interaction between MCPyV ST and the cellular phospatase subunit PP4C is essential for its effect on p38 MAPK signalling. These results provide novel opportunities for the treatment of metastatic MCC given the intense interest in p38 MAPK inhibitors as therapeutic agents.
Keywords: Merkel cell carcinoma; Merle cell polyomavirus; p38 MAPK.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Small T Antigen Drives Cell Motility via Rho-GTPase-Induced Filopodium Formation.J Virol. 2018 Jan 2;92(2):e00940-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00940-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29093086 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular sheddases are induced by Merkel cell polyomavirus small tumour antigen to mediate cell dissociation and invasiveness.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Sep 6;14(9):e1007276. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007276. eCollection 2018 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 30188954 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus small T antigen mediates microtubule destabilization to promote cell motility and migration.J Virol. 2015 Jan;89(1):35-47. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02317-14. Epub 2014 Oct 15. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 25320307 Free PMC article.
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus: a newly discovered human virus with oncogenic potential.Virology. 2013 Jan 5;435(1):118-30. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2012.09.029. Virology. 2013. PMID: 23217622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Merkel cell polyomavirus and non-Merkel cell carcinomas: guilty or circumstantial evidence?APMIS. 2020 Feb;128(2):104-120. doi: 10.1111/apm.13019. Epub 2020 Jan 28. APMIS. 2020. PMID: 31990105 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of GP-2250 on cultured virus-negative Merkel cell carcinoma cells: preliminary results.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023 Sep;149(12):10831-10840. doi: 10.1007/s00432-023-04960-3. Epub 2023 Jun 14. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37311987 Free PMC article.
-
From Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Infection to Merkel Cell Carcinoma Oncogenesis.Front Microbiol. 2021 Sep 8;12:739695. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.739695. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34566942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Virus Replication by BK Polyomavirus Small T Antigen.J Virol. 2023 Mar 30;97(3):e0007723. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00077-23. Epub 2023 Mar 14. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36916919 Free PMC article.
-
Replication Kinetics for a Reporter Merkel Cell Polyomavirus.Viruses. 2022 Feb 25;14(3):473. doi: 10.3390/v14030473. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35336880 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of 5'-Methylschweinfurthin G in Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Positive Merkel Cell Carcinoma.Viruses. 2022 Aug 23;14(9):1848. doi: 10.3390/v14091848. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146655 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

