Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels in Cancer: Focus on altered Calcium Signaling in Cancer Cells and in Tumor Progression
- PMID: 32635333
- PMCID: PMC7407875
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12071780
Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels in Cancer: Focus on altered Calcium Signaling in Cancer Cells and in Tumor Progression
Abstract
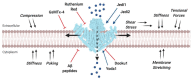
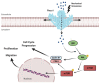
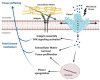
Mechanotransduction, the translation of mechanical stimuli into biological signals, is a crucial mechanism involved in the function of fundamentally all cell types. In many solid tumors, the malignant transformation is often associated with drastic changes in cell mechanical features. Extracellular matrix stiffness, invasive growth, and cell mobility are just a few hallmarks present in cancer cells that, by inducing mechanical stimuli, create positive feedbacks promoting cancer development. Among the molecular players involved in these pathophysiological processes, the mechanosensitive Ca2+-permeable Piezo channels have emerged as major transducers of mechanical stress into Ca2+ dependent signals. Piezo channels are overexpressed in several cancers, such as in breast, gastric, and bladder, whereas their downregulation has been described in other cancers. Still, the roles of mechanosensitive Piezos in cancer are somewhat puzzling. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on the pathophysiological roles of these Ca2+-permeable channels, with special emphasis on their functional involvement in different cancer types progression.
Keywords: calcium signaling; cancer progression; mechanotransduction; piezo channels.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mechanosensitive ion channels push cancer progression.Cell Calcium. 2019 Jun;80:79-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.03.007. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Cell Calcium. 2019. PMID: 30991298 Review.
-
Piezo1 Channels Are Inherently Mechanosensitive.Cell Rep. 2016 Nov 8;17(7):1739-1746. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.10.033. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27829145 Free PMC article.
-
In Touch With the Mechanosensitive Piezo Channels: Structure, Ion Permeation, and Mechanotransduction.Curr Top Membr. 2017;79:159-195. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2016.11.006. Epub 2017 Feb 21. Curr Top Membr. 2017. PMID: 28728816 Review.
-
TRPV4 and PIEZO Channels Mediate the Mechanosensing of Chondrocytes to the Biomechanical Microenvironment.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Feb 18;12(2):237. doi: 10.3390/membranes12020237. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207158 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Piezo Channels: Awesome Mechanosensitive Structures in Cellular Mechanotransduction and Their Role in Bone.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 16;22(12):6429. doi: 10.3390/ijms22126429. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34208464 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer cells can be killed mechanically or with combinations of cytoskeletal inhibitors.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 10;13:955595. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.955595. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36299893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium signalling pathways in prostate cancer initiation and progression.Nat Rev Urol. 2023 Sep;20(9):524-543. doi: 10.1038/s41585-023-00738-x. Epub 2023 Mar 24. Nat Rev Urol. 2023. PMID: 36964408 Review.
-
Selective Chemical Activation of Piezo1 in Leukemia Cell Membrane: Single Channel Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 22;22(15):7839. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157839. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360605 Free PMC article.
-
Increased PIEZO1 Expression Is Associated with Worse Clinical Outcomes in Hormone-Receptor-Negative Breast Cancer Patients.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;16(4):683. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040683. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398074 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation condition sensitizes Piezo1 mechanosensitive channel in mouse cerebellum astrocyte.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 May 25;17:1200946. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1200946. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37305437 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

