Cell-free biosensors for rapid detection of water contaminants
- PMID: 32632301
- PMCID: PMC7718425
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-020-0571-7
Cell-free biosensors for rapid detection of water contaminants
Abstract
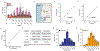
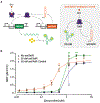
Lack of access to safe drinking water is a global problem, and methods to reliably and easily detect contaminants could be transformative. We report the development of a cell-free in vitro transcription system that uses RNA Output Sensors Activated by Ligand Induction (ROSALIND) to detect contaminants in water. A combination of highly processive RNA polymerases, allosteric protein transcription factors and synthetic DNA transcription templates regulates the synthesis of a fluorescence-activating RNA aptamer. The presence of a target contaminant induces the transcription of the aptamer, and a fluorescent signal is produced. We apply ROSALIND to detect a range of water contaminants, including antibiotics, small molecules and metals. We also show that adding RNA circuitry can invert responses, reduce crosstalk and improve sensitivity without protein engineering. The ROSALIND system can be freeze-dried for easy storage and distribution, and we apply it in the field to test municipal water supplies, demonstrating its potential use for monitoring water quality.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT
K.K.A., J.K.J. & J.B.L. have submitted a US provisional patent application (No. 62/758,242) relating to regulated in vitro transcription reactions. K.K.A., J.K.J., M.S.V., P.R.C., J.W.L., J.J.C. & J.B.L. have submitted a US provisional patent application (No. 62/838,852) relating to the preservation and stabilization of in vitro transcription reactions. K.K.A. & J.B.L. are founders and have financial interest in Stemloop, Inc. The latter interests are reviewed and managed by Northwestern University in accordance with their conflict of interest policies. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

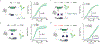
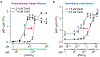
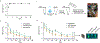
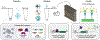
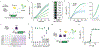


Similar articles
-
ROSALIND: Rapid Detection of Chemical Contaminants with In Vitro Transcription Factor-Based Biosensors.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2433:325-342. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1998-8_20. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34985754
-
Allosteric Regulation of DNA Circuits Enables Minimal and Rapid Biosensors of Small Molecules.ACS Synth Biol. 2021 Feb 19;10(2):371-378. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.0c00545. Epub 2021 Jan 22. ACS Synth Biol. 2021. PMID: 33481567
-
Point-of-Use Detection of Environmental Fluoride via a Cell-Free Riboswitch-Based Biosensor.ACS Synth Biol. 2020 Jan 17;9(1):10-18. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.9b00347. Epub 2019 Dec 20. ACS Synth Biol. 2020. PMID: 31829623 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering and In Vivo Applications of Riboswitches.Annu Rev Biochem. 2017 Jun 20;86:515-539. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060815-014628. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28375743 Review.
-
A review: Aptamer-based analytical strategies using the nanomaterials for environmental and human monitoring of toxic heavy metals.Talanta. 2017 Nov 1;174:619-627. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2017.06.066. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Talanta. 2017. PMID: 28738631 Review.
Cited by
-
Ten Years of the Synthetic Biology Summer Course at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory.ACS Synth Biol. 2024 Sep 20;13(9):2635-2642. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.4c00276. ACS Synth Biol. 2024. PMID: 39300908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time bioelectronic sensing of environmental contaminants.Nature. 2022 Nov;611(7936):548-553. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05356-y. Epub 2022 Nov 2. Nature. 2022. PMID: 36323787
-
Recent Trends in Chemical Sensors for Detecting Toxic Materials.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;24(2):431. doi: 10.3390/s24020431. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38257524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Wastewater monitoring comes of age.Nat Microbiol. 2022 Aug;7(8):1101-1102. doi: 10.1038/s41564-022-01201-0. Nat Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35918421 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription Factor-Based Biosensors for Detecting Pathogens.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 29;12(7):470. doi: 10.3390/bios12070470. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35884273 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- French KE, Harnessing synthetic biology for sustainable development. Nature Sustainability, 2019. 2(4): p. 250–252.
-
- Pardee K, et al., Rapid, Low-Cost Detection of Zika Virus Using Programmable Biomolecular Components. Cell, 2016. 165(5): p. 1255–1266. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

