Rotenone restrains colon cancer cell viability, motility and epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and tumorigenesis in nude mice via the PI3K/AKT pathway
- PMID: 32626924
- PMCID: PMC7307809
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4637
Rotenone restrains colon cancer cell viability, motility and epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and tumorigenesis in nude mice via the PI3K/AKT pathway
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Rotenone restrains colon cancer cell viability, motility and epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and tumorigenesis in nude mice via the PI3K/AKT pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2024 Feb;53(2):16. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5340. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38099365 Free PMC article.
Abstract
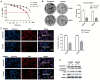
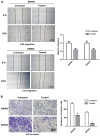
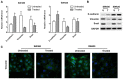
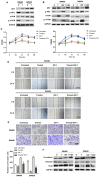
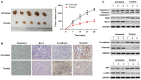
Rotenone, a natural hydrophobic pesticide, has been reported to display anticancer activity in a variety of cancer cells. However, the mechanism of rotenone on colon cancer (CC) cell migration, invasion and metastasis is still unknown. In the present study, the cytotoxicity of rotenone on CC cells were detected by the Cell Counting Kit‑8 assay and confirmed by clone formation assay. The effects of rotenone on CC cell invasion and migration activity were determined in vitro by Transwell invasion and wound healing assays, respectively. In addition, to reveal whether rotenone affected the epithelial‑mesenchymal‑transition (EMT) process, reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR, western blotting and immunofluorescence assays were used to detect the expression of EMT markers. The expression levels of the key markers of the PI3K/AKT pathway after rotenone treatment alone or in combination with a PI3K/AKT signaling activator in CC were also detected by western blotting. Finally, the in vivo antitumor effects of rotenone were evaluated in a subcutaneous xenotransplant tumor model treated with an intraperitoneal injection of rotenone. The results of the present study demonstrated that rotenone treatment induced CC cell cytotoxicity and greater effects were observed with increasing concentrations and inhibited cell proliferation compared with untreated cells. In vitro cell function assays revealed that rotenone inhibited CC cell migration, invasion and EMT compared with untreated cells. Mechanically, the phosphorylation levels of AKT and mTOR were downregulated in rotenone‑treated CC cells compared with untreated cells. Additionally, AKT and mTOR phosphorylation levels were increased by the PI3K/AKT signaling activator insulin‑like growth factor 1 (IGF‑1), which was reversed by rotenone treatment. The cell function assays confirmed that the IGF‑1‑activated cell proliferation, migration and invasion were decreased by rotenone treatment. These results indicated that rotenone affected CC cell proliferation and metastatic capabilities by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. In addition, rotenone inhibited tumor growth and metastatic capability of CC, which was confirmed in a xenograft mouse model. In conclusion, the present study revealed that rotenone inhibited CC cell viability, motility, EMT and metastasis in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rotenone restrains the proliferation, motility and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of colon cancer cells and the tumourigenesis in nude mice via PI3K/AKT pathway.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020 Aug;47(8):1484-1494. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13320. Epub 2020 May 11. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2020. Retraction in: Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2025 Feb;52(2):e70014. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.70014 PMID: 32282954 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
AIM2 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and migration, and promotes the apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by inactivating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2022 Feb;25(2):53. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12569. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Mol Med Rep. 2022. PMID: 34913077 Free PMC article.
-
SSPH I, A Novel Anti-cancer Saponin, Inhibits EMT and Invasion and Migration of NSCLC by Suppressing MAPK/ERK1/2 and PI3K/AKT/ mTOR Signaling Pathways.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024;19(4):543-555. doi: 10.2174/0115748928283132240103073039. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38305308
-
Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: the framework of malignant behavior.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Jun;47(6):4587-4629. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05435-1. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32333246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of Ferulic Acid in PI3K/AKT Pathway and Research in Glioblastoma.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 May;30(5):104-109. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 38290467 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiproliferative Activities and SwissADME Predictions of Physicochemical Properties of Carbonyl Group-Modified Rotenone Analogues.ChemistryOpen. 2024 Jan;13(1):e202300087. doi: 10.1002/open.202300087. Epub 2023 Aug 17. ChemistryOpen. 2024. PMID: 37590423 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Tumorigenesis and Progression.Cells. 2024 Mar 2;13(5):441. doi: 10.3390/cells13050441. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38474405 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct effects of different doses of kaempferol on D‑GalN/LPS‑induced ALF depend on the autophagy pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Sep;24(3):682. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12321. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34318900 Free PMC article.
-
Tephrosin Suppresses the Chemoresistance of Paclitaxel-Resistant Ovarian Cancer via Inhibition of FGFR1 Signaling Pathway.Biomedicines. 2023 Nov 27;11(12):3155. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123155. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137377 Free PMC article.
-
Stemness signature and targeted therapeutic drugs identification for Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Sci Data. 2023 Nov 20;10(1):815. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02709-8. Sci Data. 2023. PMID: 37985782 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

