Research trends on the relationship between Microbiota and Gastric Cancer: A Bibliometric Analysis from 2000 to 2019
- PMID: 32626529
- PMCID: PMC7330707
- DOI: 10.7150/jca.44126
Research trends on the relationship between Microbiota and Gastric Cancer: A Bibliometric Analysis from 2000 to 2019
Abstract
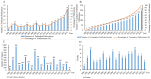
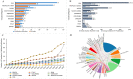
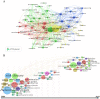
Background: Hundreds of studies have found that the microbiota contributes to the development of gastric cancer in the past two decades. This study aimed to access the research trends of microbiota and gastric cancer. Materials and Methods: Publications from January 1, 2000 to December 31, 2019 were retrieved from the Web of Science Core Collection database and screened according to inclusion criteria. Different kinds of software, SPSS21.0, HistCite, VOSviewer, CiteSpace, and the online bibliometric analysis platform were used to evaluate and visualize the results. Results: A total of 196 publications were finally identified, and the annual number of publications showed an increasing trend. These publications were from 44 countries and the USA showed its dominant position in publication outputs, H-index, total citations, and international collaborations. The journal of Helicobacter was the most productive journal. Correa P and Peek RM published the most papers, and the most productive institution was Vanderbilt University. The keyword of "Helicobacter pylori" ranked first in research frontiers and appeared earlier, and the keyword of "microbiota" began to appear in the past 3 to 5 years. Conclusion: The annual number of publications would continue to grow. Besides the traditional Helicobacter pylori related researches, future research hotspots will focus on microbiota and its mechanism of action.
Keywords: Bibliometric Analysis; Gastric Cancer; Microbiota; Research trend.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Hotspots and frontiers in Helicobacter pylori biofilm research: A bibliometric and visualization analysis from 1998 to 2023.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 13;10(6):e27884. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27884. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38533074 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends on the relationship between gut microbiota and colorectal cancer: A bibliometric analysis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Jan 9;12:1027448. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.1027448. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36699721 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends on the relationship between Helicobacter pylori and microbiota: A bibliometric analysis.Helicobacter. 2023 Dec;28(6):e13021. doi: 10.1111/hel.13021. Epub 2023 Sep 11. Helicobacter. 2023. PMID: 37697432
-
States and hotspots in Helicobacter pylori research from 2002 to 2021: A bibliometric analysis.Helicobacter. 2023 Aug;28(4):e12986. doi: 10.1111/hel.12986. Epub 2023 May 3. Helicobacter. 2023. PMID: 37133423 Review.
-
Trends in Helicobacter pylori-related gastric ulcer research from 2012 to 2022: A bibliometric and visual analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 23;9:1027534. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1027534. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36507534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A bibliometric analysis of autophagy in lung diseases from 2012 to 2021.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 16;13:1092575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1092575. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591291 Free PMC article.
-
Studies related to osteosarcoma and metabolism from 1990 to 2022: A visual analysis and bibliometric study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 6;14:1144747. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1144747. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36950694 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends on nanomaterials in gastric cancer: a bibliometric analysis from 2004 to 2023.J Nanobiotechnology. 2023 Aug 2;21(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12951-023-02033-8. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023. PMID: 37533041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging trends and focus on the link between gut microbiota and type 1 diabetes: A bibliometric and visualization analysis.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 9;14:1137595. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1137595. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36970681 Free PMC article.
-
Hotspots and frontiers in Helicobacter pylori biofilm research: A bibliometric and visualization analysis from 1998 to 2023.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 13;10(6):e27884. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27884. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38533074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Corley DA, Kubo A. Influence of site classification on cancer incidence rates: an analysis of gastric cardia carcinomas. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2004;96:1383–1387. - PubMed
-
- Raza MH, Gul K, Arshad A, Riaz N, Waheed U, Rauf A. et al. Microbiota in cancer development and treatment. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2019;145:49–63. - PubMed
-
- Villanueva-Millán MJ, Pérez-Matute P, Oteo JA. Gut microbiota: a key player in health and disease. A review focused on obesity. J Physiol Biochem. 2015;71:509–525. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

