Lipid nanoparticle technology for therapeutic gene regulation in the liver
- PMID: 32622021
- PMCID: PMC7329694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.06.026
Lipid nanoparticle technology for therapeutic gene regulation in the liver
Abstract
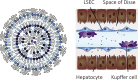
Hereditary genetic disorders, cancer, and infectious diseases of the liver affect millions of people around the globe and are a major public health burden. Most contemporary treatments offer limited relief as they generally aim to alleviate disease symptoms. Targeting the root cause of diseases originating in the liver by regulating malfunctioning genes with nucleic acid-based drugs holds great promise as a therapeutic approach. However, employing nucleic acid therapeutics in vivo is challenging due to their unfavorable characteristics. Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) delivery technology is a revolutionary development that has enabled clinical translation of gene therapies. LNPs can deliver siRNA, mRNA, DNA, or gene-editing complexes, providing opportunities to treat hepatic diseases by silencing pathogenic genes, expressing therapeutic proteins, or correcting genetic defects. Here we discuss the state-of-the-art LNP technology for hepatic gene therapy including formulation design parameters, production methods, preclinical development and clinical translation.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; DNA; Gene therapy; gene editing; gene expression; gene silencing; guide RNA (gRNA); hepatocyte; lipid nanoparticle (LNP); lipids; liver; messenger RNA (mRNA); small interfering RNA (siRNA).
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

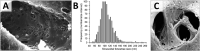


Similar articles
-
Lipid Nanoparticle Technology for Clinical Translation of siRNA Therapeutics.Acc Chem Res. 2019 Sep 17;52(9):2435-2444. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00368. Epub 2019 Aug 9. Acc Chem Res. 2019. PMID: 31397996 Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticle technology-mediated therapeutic gene manipulation in the eyes.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jun 3;35(3):102236. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102236. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39005878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid nanoparticles for short interfering RNA delivery.Adv Genet. 2014;88:71-110. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800148-6.00004-3. Adv Genet. 2014. PMID: 25409604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid Nanoparticles Enabling Gene Therapies: From Concepts to Clinical Utility.Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018 Jun;28(3):146-157. doi: 10.1089/nat.2018.0721. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2018. PMID: 29683383 Review.
-
Developing Biodegradable Lipid Nanoparticles for Intracellular mRNA Delivery and Genome Editing.Acc Chem Res. 2021 Nov 2;54(21):4001-4011. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.1c00500. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Acc Chem Res. 2021. PMID: 34668716 Review.
Cited by
-
Navigating the CRISPR/Cas Landscape for Enhanced Diagnosis and Treatment of Wilson's Disease.Cells. 2024 Jul 18;13(14):1214. doi: 10.3390/cells13141214. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39056796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liver-Targeting Nanoplatforms for the Induction of Immune Tolerance.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Dec 26;14(1):67. doi: 10.3390/nano14010067. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cholesterol Conjugates of Small Interfering RNA: Linkers and Patterns of Modification.Molecules. 2024 Feb 8;29(4):786. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040786. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398538 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-nanoparticle-enabled nucleic acid therapeutics for liver disorders.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Jul;14(7):2885-2900. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.04.015. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 39027251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 using lipid nanoparticles enables antithrombin gene editing for sustainable hemophilia A and B therapy.Sci Adv. 2022 Jan 21;8(3):eabj6901. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abj6901. Epub 2022 Jan 21. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35061543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams R., Aspinall R., Bellis M., Camps-Walsh G., Cramp M., Dhawan A., Ferguson J., Forton D., Foster G., Gilmore I., Hickman M., Hudson M., Kelly D., Langford A., Lombard M., Longworth L., Martin N., Moriarty K., Newsome P., O’Grady J., Pryke R., Rutter H., Ryder S., Sheron N., Smith T. Addressing liver disease in the UK: a blueprint for attaining excellence in health care and reducing premature mortality from lifestyle issues of excess consumption of alcohol, obesity, and viral hepatitis. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2014;384:1953–1997. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61838-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

