Neurosyphilis revealed by compressive cervical spine syphilitic gumma: a case report
- PMID: 32606288
- PMCID: PMC7324907
- DOI: 10.1038/s41394-020-0303-8
Neurosyphilis revealed by compressive cervical spine syphilitic gumma: a case report
Abstract
Introduction: Neurosyphilis is a sexually transmitted disease secondary to the invasion of the central nervous system by the Treponema pallidum. The spinal syphilitic gumma is rare.
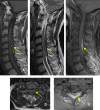
Case presentation: We report a case of extradural cervical spinal syphilitic gumma revealed by spinal cord compression in a 58-year-old male. The epidural lesion was removed via a posterior approach. Histological examination revealed syphilis. Syphilis serologies were positive. Brain MRI showed an associated cerebro-meningeal syphilitic gumma. Antibiotic regime based on aqueous penicillin G was introduced for 14 days.
Discussion: Currently, there is an increase in the frequency of syphilis and changes in its clinical manifestations. Neurosyphilis can take atypical forms. Spinal syphilitic gumma is a rare manifestation and its association with cerebral involvement is exceptional. Diagnosis is based on serologies in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid. The place of imagery, especially magnetic resonance imaging, is essential. Neurosyphilis should be discussed as a possible differential diagnosis in evaluation of spinal and cerebral lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spinal Intramedullary Syphilitic Gumma: An Unusual Presentation of Neurosyphilis.World Neurosurg. 2016 Nov;95:622.e17-622.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2016.07.049. Epub 2016 Jul 21. World Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 27452967
-
Spinal Cord Syphilitic Gumma Presenting with Brown-Séquard Syndrome: A Case Report and Literature Review.Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019 Mar;49(2):265-270. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019. PMID: 31028074 Review.
-
[Spinal cord compression due to intraspinal syphilitic gumma in one patient. Clinical case].Acta Ortop Mex. 2012 May-Jun;26(3):197-201. Acta Ortop Mex. 2012. PMID: 23320318 Spanish.
-
[A case of cerebral syphilitic gumma mimicking a brain tumor].Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014;54(9):738-42. doi: 10.5692/clinicalneurol.54.738. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 2014. PMID: 25283829 Japanese.
-
Cerebral syphilitic gumma: a case report and review of the literature.Neurol Sci. 2012 Oct;33(5):1179-81. doi: 10.1007/s10072-011-0878-8. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Neurol Sci. 2012. PMID: 22167653 Review.
Cited by
-
Contribution of advanced neuroimaging in diagnosis of cerebral syphilitic gumma: a case report.Front Neurosci. 2024 Aug 14;18:1442176. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1442176. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39206117 Free PMC article.
-
A large screen identifies beta-lactam antibiotics which can be repurposed to target the syphilis agent.NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2023;1(1):4. doi: 10.1038/s44259-023-00006-3. Epub 2023 Jun 1. NPJ Antimicrob Resist. 2023. PMID: 38686211 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in the Diagnosis of Tertiary Syphilis: Case Report with Literature Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 17;19(24):16992. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416992. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36554872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complete bone fusion in failed back surgery syndrome using teriparatide in neurosyphilis: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022 Dec;101:107816. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2022.107816. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36459850 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple Spinal Syphilitic Gummas Diagnosed by Postoperative Histopathology and Antibiotic Responsiveness: A Case Report.NMC Case Rep J. 2021 Sep 16;8(1):637-643. doi: 10.2176/nmccrj.cr.2021-0098. eCollection 2021. NMC Case Rep J. 2021. PMID: 35079528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang YH, Shi QX, Xu MM, Chen CZ, Yang ML, Li JJ, et al. Spinal cord syphilitic gumma presenting with brown-Séquard syndrome: a case report and literature review. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 2019;49:265–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

