Updates of Cardiovascular Manifestations in COVID-19: Korean Experience to Broaden Worldwide Perspectives
- PMID: 32588565
- PMCID: PMC7321759
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2020.0205
Updates of Cardiovascular Manifestations in COVID-19: Korean Experience to Broaden Worldwide Perspectives
Abstract
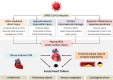
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has spread worldwide. Not just respiratory complications such as pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, cardiac manifestations have drawn attention due to the increased risk of mortality and morbidity related to SARS-CoV-2 infections. The mechanisms of the cardiac injury related to SARS-CoV-2 infections have been direct cardiac injury caused by angiotensin converting enzyme 2, hypoxemia, microvascular damage, and a systemic inflammatory response. Stress induced cardiomyopathy in a critically ill condition and acute coronary syndrome due to a vulnerable plaque rupture with coagulopathy can finally lead to acute heart failure with further cardiac manifestations. When dealing with the highly contagious viral disease-related cardiac manifestations, we should carefully apply the diagnostic and therapeutic methods to achieve the best therapeutic results without adding any risk of disease transmission.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cardiac injury; Cardiac manifestation; Coronavirus; Heart; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020. The Korean Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Myocardial injury and COVID-19: Possible mechanisms.Life Sci. 2020 Jul 15;253:117723. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117723. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32360126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Description and Proposed Management of the Acute COVID-19 Cardiovascular Syndrome.Circulation. 2020 Jun 9;141(23):1903-1914. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.047349. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Circulation. 2020. PMID: 32297796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Testing the efficacy and safety of BIO101, for the prevention of respiratory deterioration, in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia (COVA study): a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2021 Jan 11;22(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04998-5. Trials. 2021. PMID: 33430924 Free PMC article.
-
Manifestations and Mechanism of SARS-CoV2 Mediated Cardiac Injury.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;18(7):2703-2713. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.69677. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35541905 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Cardiac Injury in Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Other Viral Infections-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Crit Care Med. 2021 Sep 1;49(9):1558-1566. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005026. Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33870918
Cited by
-
Getting to the Heart of the Matter: Myocardial Injury, Coagulopathy, and Other Potential Cardiovascular Implications of COVID-19.Int J Vasc Med. 2021 Apr 22;2021:6693895. doi: 10.1155/2021/6693895. eCollection 2021. Int J Vasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34035963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnic Difference of Thrombogenicity in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease: a Pandora Box to Explain Prognostic Differences.Korean Circ J. 2021 Mar;51(3):202-221. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2020.0537. Korean Circ J. 2021. PMID: 33655720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis of cardiac markers for predictive factors on severity and mortality of COVID-19.Int J Infect Dis. 2021 Apr;105:551-559. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.03.008. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Int J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33711519 Free PMC article.
-
Neuromodulation Strategies to Reduce Inflammation and Improve Lung Complications in COVID-19 Patients.Front Neurol. 2022 Jul 14;13:897124. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.897124. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35911909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Author's Reply to Heart Transplantation to Fulminant Myocarditis during COVID-19 Outbreak.Korean Circ J. 2020 Nov;50(11):1041-1042. doi: 10.4070/kcj.2020.3571. Korean Circ J. 2020. PMID: 33118338 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak [Internet] Geneva: World Health Organization; c2020. [cited 2020 May 5]. Available from: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323:1239. - PubMed
-
- Thomson B. The COVID-19 pandemic: a global natural experiment. Circulation. 2020 [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

