Methodological and reporting quality evaluation of meta-analyses on the Chinese herbal preparation Zheng Qing Feng Tong Ning for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 32586308
- PMCID: PMC7318442
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-020-02978-5
Methodological and reporting quality evaluation of meta-analyses on the Chinese herbal preparation Zheng Qing Feng Tong Ning for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Zheng Qing Feng Tong Ning (ZQFTN) is a sinomenine (SIN) preparation that has been used in clinical practice. Our study aimed to assess the methodological and reporting quality of meta-analyses on the Chinese herbal formula ZQFTN for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
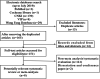
Methods: Systematic searches were carried out with the 5 following electronic databases from inception to July 2019: China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang, VIP database for Chinese technical periodicals (VIP), Cochrane Library and PubMed. The quality of the methodology and reporting was measured with the assessment of multiple systematic reviews 2 (AMSTAR 2) scale, the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement and the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE).
Results: Eight studies were identified. Among the 16 items of the AMSTAR 2 scale, four items were optimally reported ("Y" =100% of the items), and another four items were poorly reported ("Y" =0% of the items). Only 2 studies received a good overall score ("Y" ≥50% of the items). Regarding the PRISMA statement, the scores of 5 studies were lower than the average score (17.69), indicating that the quality of the reports was very low. In terms of the GRADE, none of the 61 results were of high quality (0.0%). Fifteen results were of medium quality (25%), 34 were of low quality (55%), and 12 were of very low quality (20%). Among the five downgrading factors, deviation risk (n = 61, 100%) was the most common downgrading factor, followed by inconsistency (n = 30, 50%), publication bias (n = 17, 28%), inaccuracy (n = 11, 18%) and indirectness (n = 0, 0%).
Conclusions: The methodological and reporting quality of the meta-analyses and systematic reviews in the included studies are less than optimal, and researchers should undergo additional training and follow the AMSTAR 2 scale, PRISMA statement and GRADE to design high-quality studies in the future.
Keywords: Meta-analysis; Methodology; Reporting quality; Rheumatoid arthritis; Sinomenine; Zheng Qing Feng Tong Ning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Total glucosides of paeony for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A methodological and reporting quality evaluation of systematic reviews and meta-analyses.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Nov;88:106920. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106920. Epub 2020 Aug 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32871476
-
Shenfu injection for heart failure based on the AMSTAR-2, PRISMA, and GRADE tools.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jun;10(6):6535-6555. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1073. Epub 2021 Jun 15. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34154360
-
A Methodological and Reporting Quality Assessment of Systematic Reviews/Meta-Analyses about Chinese Medical Treatment for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2020 Sep 24;2020:3868057. doi: 10.1155/2020/3868057. eCollection 2020. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 33029131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of recurrent respiratory tract infections in children: an overview of systematic reviews and Meta-analyses.J Tradit Chin Med. 2024 Oct;44(5):871-884. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240806.007. J Tradit Chin Med. 2024. PMID: 39380218 Free PMC article.
-
Chinese herbal medicine for the treatment of primary hypertension: a methodology overview of systematic reviews.Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 20;5(1):180. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0353-y. Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27760557 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A systematic evaluation of methodological and reporting quality of meta-analysis published in the field of gastrointestinal endoscopy.Surg Endosc. 2023 Feb;37(2):807-816. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09570-7. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Surg Endosc. 2023. PMID: 36050611 Review.
-
Digital Biomarker-Based Interventions: Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews.J Med Internet Res. 2022 Dec 21;24(12):e41042. doi: 10.2196/41042. J Med Internet Res. 2022. PMID: 36542427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhu LF, Feng YR, Xu DY. Advances in research on quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Arthritis. 2018;7:76–80.
-
- McInnes IB, Kim HY, Lee SH, Mandel D, Song YW, Connell CA, Luo Z, Brosnan MJ, Zuckerman A, Zwillich SH, Bradley JD. Open-label tofacitinib and double-blind atorvastatin in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a randomised study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73:124–131. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical