Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential
- PMID: 32585269
- PMCID: PMC7308007
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.190
Exopolysaccharides from probiotic bacteria and their health potential
Abstract
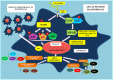
Exopolysaccharides (EPS) are extracellular macromolecules excreted as tightly bound capsule or loosely attached slime layer in microorganisms. They play most prominent role against desiccation, phagocytosis, cell recognition, phage attack, antibiotics or toxic compounds and osmotic stress. In the last few decades, natural polymers have gained much attention among scientific communities owing to their therapeutic potential. In particular the EPS retrieved from probiotic bacteria with varied carbohydrate compositions possess a plenty of beneficial properties. Different probiotic microbes have unique behavior in expressing their capability to display significant health promoting characteristics in the form of polysaccharides. In this new era of alternative medicines, these polysaccharides are considered as substitutes for synthetic drugs. The EPS finds applications in various fields like textiles, cosmetics, bioremediation, food and therapeutics. The present review is focused on sources, chemical composition, biosynthetic pathways of EPS and their biological potential. More attention has been given to the scientific investigations on antimicrobial, antitumor, anti-biofilm, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities.
Keywords: Biosynthetic pathway; Exopolysaccharides; Health potential; Lactic acid bacteria; Probiotics; Structure.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides in vitro: A review.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Feb 1;253:117308. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117308. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33278957 Review.
-
Functional and health-promoting properties of probiotics' exopolysaccharides; isolation, characterization, and applications in the food industry.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(26):8194-8225. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2022.2047883. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 35266799 Review.
-
A comprehensive review of anticancer, immunomodulatory and health beneficial effects of the lactic acid bacteria exopolysaccharides.Carbohydr Polym. 2019 Aug 1;217:79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.04.025. Epub 2019 Apr 20. Carbohydr Polym. 2019. PMID: 31079688 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on α-D-Glucans: Structural and functional diversity, derivatization and bioapplications.Carbohydr Res. 2021 May;503:108297. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108297. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Carbohydr Res. 2021. PMID: 33813321 Review.
-
Extracellular polysaccharide derived from potential probiotic strain with antioxidant and antibacterial activities as a prebiotic agent to control pathogenic bacterial biofilm formation.Microb Pathog. 2017 Aug;109:214-220. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.05.046. Epub 2017 Jun 2. Microb Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28583888
Cited by
-
Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CA15 (DSM 33960) as a Candidate Probiotic Strain for Human Health.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 19;14(22):4902. doi: 10.3390/nu14224902. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432588 Free PMC article.
-
Heat-killed probiotic Levilactobacillus brevis MKAK9 and its exopolysaccharide promote longevity by modulating aging hallmarks and enhancing immune responses in Caenorhabditis elegans.Immun Ageing. 2024 Aug 2;21(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12979-024-00457-w. Immun Ageing. 2024. PMID: 39095841 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple biological characteristics and functions of intestinal biofilm extracellular polymers: friend or foe?Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 19;15:1445630. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1445630. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39224216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production and Characterization of New Biosurfactants/Bioemulsifiers from Pantoea alhagi and Their Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Anti-Biofilm Potentiality Evaluations.Molecules. 2023 Feb 17;28(4):1912. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041912. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838900 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Polymeric Substances: Still Promising Antivirals.Viruses. 2022 Jun 19;14(6):1337. doi: 10.3390/v14061337. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35746808 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dilna S.V., Surya H., Aswathy R.G., Varsha K.K., Sakthikumar D.N., Pandey A., Nampoothiri K.M. Characterization of an exopolysaccharide with potential health-benefit properties from a probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum RJF4. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 2015;64:1179–1186. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.07.040. - DOI
-
- Majee S.B., Avlani D., Biswas G.R. Vol. 7. 2017. Rheological Behavior and Pharmaceutical Applications of Bacterial Exopolysaccharides; pp. 224–232. - DOI
-
- Ziadi M., Bouzaiene T., M’Hir S., Zaafouri K., Mokhtar F., Hamdi M., Boisset-Helbert C. Evaluation of the efficiency of ethanol precipitation and ultrafiltration on the purification and characteristics of exopolysaccharides produced by three lactic acid bacteria. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018;2018 doi: 10.1155/2018/1896240. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

