Rationally Designed Polypharmacology: α-Helix Mimetics as Dual Inhibitors of the Oncoproteins Mcl-1 and HDM2
- PMID: 32583936
- PMCID: PMC8477420
- DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.202000278
Rationally Designed Polypharmacology: α-Helix Mimetics as Dual Inhibitors of the Oncoproteins Mcl-1 and HDM2
Abstract
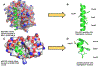
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs), many of which are dominated by α-helical recognition domains, play key roles in many essential cellular processes, and the dysregulation of these interactions can cause detrimental effects. For instance, aberrant PPIs involving the Bcl-2 protein family can lead to several diseases including cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes. Interactions between Bcl-2 pro-life proteins, such as Mcl-1, and pro-death proteins, such as Bim, regulate the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. p53, a tumor-suppressor protein, also has a pivotal role in apoptosis and is negatively regulated by its E3 ubiquitin ligase HDM2. Both Mcl-1 and HDM2 are upregulated in numerous cancers, and, interestingly, there is crosstalk between both protein pathways. Recently, synergy has been observed between Mcl-1 and HDM2 inhibitors. Towards the development of new anticancer drugs, we herein describe a polypharmacology approach for the dual inhibition of Mcl-1 and HDM2 by employing three densely functionalized isoxazoles, pyrazoles, and thiazoles as mimetics of key α-helical domains of their partner proteins.
Keywords: apoptosis; cancer; heterocycles; polypharmacology; protein-protein interactions.
© 2020 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
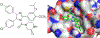
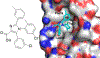


Similar articles
-
Novel Mcl-1/Bcl-2 dual inhibitors created by the structure-based hybridization of drug-divided building blocks and a fragment deconstructed from a known two-face BH3 mimetic.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2015 Feb;348(2):89-99. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201400296. Epub 2015 Jan 13. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2015. PMID: 25641608
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of dual Bcl-2/Mcl-1 inhibitors bearing 2-(1H-indol-4-yl)benzoic acid scaffold.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Sep 1;47:128215. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128215. Epub 2021 Jun 19. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34153472
-
Probing Protein Surfaces: QSAR Analysis with Helix Mimetics.Chembiochem. 2016 Apr 15;17(8):768-73. doi: 10.1002/cbic.201500504. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Chembiochem. 2016. PMID: 26690307 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors of the p53-HDM2 interaction for the treatment of cancer.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008 Dec;17(12):1865-82. doi: 10.1517/13543780802493366. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2008. PMID: 19012502 Review.
-
Small molecule protein-protein inhibitors for the p53-MDM2 interaction.Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(10):952-60. doi: 10.2174/156802607780906762. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17508926 Review.
Cited by
-
Discovery of spirooxindole-derived small-molecule compounds as novel HDAC/MDM2 dual inhibitors and investigation of their anticancer activity.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 4;12:972372. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.972372. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992773 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of N-sulfonylated aminosalicylic acids as dual MCL-1/BCL-xL inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Oct 27;14(1):103-112. doi: 10.1039/d2md00277a. eCollection 2023 Jan 25. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36760746 Free PMC article.
-
Scaffold hopping from indoles to indazoles yields dual MCL-1/BCL-2 inhibitors from MCL-1 selective leads.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Jun 3;13(8):963-969. doi: 10.1039/d2md00095d. eCollection 2022 Aug 17. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36092148 Free PMC article.
-
Recent applications of covalent chemistries in protein-protein interaction inhibitors.RSC Med Chem. 2022 Jun 3;13(8):921-928. doi: 10.1039/d2md00112h. eCollection 2022 Aug 17. RSC Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36092144 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

