Whole-genome sequencing of patients with rare diseases in a national health system
- PMID: 32581362
- PMCID: PMC7610553
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2434-2
Whole-genome sequencing of patients with rare diseases in a national health system
Abstract
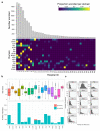
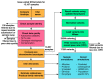
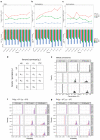
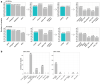
Most patients with rare diseases do not receive a molecular diagnosis and the aetiological variants and causative genes for more than half such disorders remain to be discovered1. Here we used whole-genome sequencing (WGS) in a national health system to streamline diagnosis and to discover unknown aetiological variants in the coding and non-coding regions of the genome. We generated WGS data for 13,037 participants, of whom 9,802 had a rare disease, and provided a genetic diagnosis to 1,138 of the 7,065 extensively phenotyped participants. We identified 95 Mendelian associations between genes and rare diseases, of which 11 have been discovered since 2015 and at least 79 are confirmed to be aetiological. By generating WGS data of UK Biobank participants2, we found that rare alleles can explain the presence of some individuals in the tails of a quantitative trait for red blood cells. Finally, we identified four novel non-coding variants that cause disease through the disruption of transcription of ARPC1B, GATA1, LRBA and MPL. Our study demonstrates a synergy by using WGS for diagnosis and aetiological discovery in routine healthcare.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Diagnostic and clinical utility of whole genome sequencing in a cohort of undiagnosed Chinese families with rare diseases.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 18;9(1):19365. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55832-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31852928 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing association analysis of quantitative red blood cell phenotypes: The NHLBI TOPMed program.Am J Hum Genet. 2021 May 6;108(5):874-893. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.04.003. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Am J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33887194 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of whole genome sequencing into a healthcare setting: high diagnostic rates across multiple clinical entities in 3219 rare disease patients.Genome Med. 2021 Mar 17;13(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00855-5. Genome Med. 2021. PMID: 33726816 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome sequencing as a first-tier diagnostic framework for rare genetic diseases.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021 Dec;246(24):2610-2617. doi: 10.1177/15353702211040046. Epub 2021 Sep 15. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021. PMID: 34521224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges in the diagnosis and discovery of rare genetic disorders using contemporary sequencing technologies.Brief Funct Genomics. 2020 Jul 29;19(4):243-258. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/elaa009. Brief Funct Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32393978 Review.
Cited by
-
Rare variant analysis of 4241 pulmonary arterial hypertension cases from an international consortium implicates FBLN2, PDGFD, and rare de novo variants in PAH.Genome Med. 2021 May 10;13(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13073-021-00891-1. Genome Med. 2021. PMID: 33971972 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics of germline variant discovery for rare disease diagnostics: current approaches and remaining challenges.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Jan 22;25(2):bbad508. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad508. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38271481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rare heterozygous variants in paediatric steroid resistant nephrotic syndrome - a population-based analysis of their significance.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 10;14(1):18568. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-68837-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39127776 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of whole genome sequencing utility in identifying driver alterations in cancer genome.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 12;14(1):23898. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-74272-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39396060 Free PMC article.
-
Practical guide for managing large-scale human genome data in research.J Hum Genet. 2021 Jan;66(1):39-52. doi: 10.1038/s10038-020-00862-1. Epub 2020 Oct 23. J Hum Genet. 2021. PMID: 33097812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ferreira CR. The burden of rare diseases. Am J Med Genet A. 2019 Jun;179(6):885–892. - PubMed
-
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015 May;17(5):405–24. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 202747/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RP-2016-07-019/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- MR/N025431/2/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0800571/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 201064/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/J011711/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1002528/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204809/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G0701386/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 204809/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/S025502/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT108749/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 107469/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- FS/18/53/33863/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 29034/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 098519/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 202747/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CH/1992001/6764/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- MR/N025431/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N010035/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/K020919/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FS/18/52/33808/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 28051/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G1000848/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/P02002X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L019027/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_EX_MR/M009203/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1002570/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/M012212/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_18030/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_15080/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/R002363/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT098519MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- WT200990/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 309548/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- 212219/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- SP/12/12/29836/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 107469/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 109915/Z/15/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 095908/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/M009203/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/S021329/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 108749/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_U120085815/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L006340/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- RG/16/4/32218/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 212219/Z/18/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MR/R013942/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 109915/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- 201064/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_14089/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 200990/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

