Impact of Coenzyme Q10 Administration on Lead Acetate-Induced Testicular Damage in Rats
- PMID: 32566085
- PMCID: PMC7290879
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/4981386
Impact of Coenzyme Q10 Administration on Lead Acetate-Induced Testicular Damage in Rats
Abstract
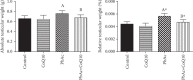
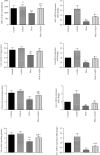
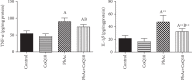
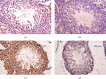
Exposure to lead (Pb) causes multiorgan dysfunction including reproductive impairments. Here, we examined the protective effects of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) administration on testicular injury induced by lead acetate (PbAc) exposure in rats. This study employed four experimental groups (n = 7) that underwent seven days of treatment as follows: control group intraperitoneally (i.p.) treated with 0.1 ml of 0.9% NaCl containing 1% Tween 80 (v : v), CoQ10 group that was i.p. injected with 10 mg/kg CoQ10, PbAc group that was i.p. treated with PbAc (20 mg/kg), and PbAc+CoQ10 group that was i.p. injected with CoQ10 2 h after PbAc. PbAc injection resulted in increasing residual Pb levels in the testis and reducing testosterone, luteinizing hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone levels. Additionally, PbAc exposure resulted in significant oxidative damage to the tissues on the testes. PbAc raised the levels of prooxidants (malondialdehyde and nitric oxide) and reduced the amount of endogenous antioxidative proteins (glutathione and its derivative enzymes, catalase, and superoxide dismutase) available in the cell. Moreover, PbAc induced the inflammatory response as evidenced by the upregulation of inflammatory mediators (tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1 beta). Further, PbAc treatment induced apoptosis in the testicular cells, as indicated by an increase in Bax and caspase 3 expression, and reduced Bcl2 expression. CoQ10 supplementation improved testicular function by inhibiting Pb accumulation, oxidative stress, inflammation, cell death, and histopathological changes following PbAc exposure. Our findings suggest that CoQ10 can act as a natural therapeutic agent to protect against the reproductive impairments associated with PbAc exposure.
Copyright © 2020 Manal El-khadragy et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

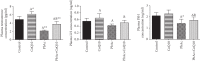
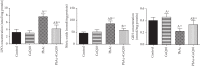
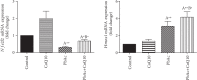
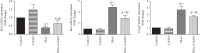
Similar articles
-
The Neuroprotective Role of Coenzyme Q10 Against Lead Acetate-Induced Neurotoxicity Is Mediated by Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Apoptotic Activities.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Aug 13;16(16):2895. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16162895. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31412628 Free PMC article.
-
Green Coffea arabica Extract Ameliorates Testicular Injury in High-Fat Diet/Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Rats.J Diabetes Res. 2020 Jun 12;2020:6762709. doi: 10.1155/2020/6762709. eCollection 2020. J Diabetes Res. 2020. PMID: 32626781 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin protects against testicular injury induced by lead acetate by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.IUBMB Life. 2020 Aug;72(8):1787-1798. doi: 10.1002/iub.2311. Epub 2020 Jun 1. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32478470
-
Involvement of Nrf2-PPAR-γ signaling in Coenzyme Q10 protecting effect against methotrexate-induced testicular oxidative damage.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Mar 10;129:111566. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111566. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38364740
-
Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation Improves Adipokine Levels and Alleviates Inflammation and Lipid Peroxidation in Conditions of Metabolic Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 4;21(9):3247. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093247. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32375340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and/or cadmium chloride oral exposure on testicular morphology, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in rats: Ameliorative role of co-enzyme Q10.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 3;10(1):e24049. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24049. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38268588 Free PMC article.
-
The Palliative and Antioxidant Effects of Hesperidin against Lead-Acetate-Induced Testicular Injury in Male Wistar Rats.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 26;11(9):2390. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092390. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760831 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy via antioxidant and anti-apoptotic pathway.Tissue Barriers. 2023 Jan 2;11(1):2019504. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2021.2019504. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Tissue Barriers. 2023. PMID: 34939895 Free PMC article.
-
Naringin mitigates testicular injury and associated neuronal toxicity in lead-exposed cockerel chicks.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2024 Jan-Feb;14(1):50-63. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2023.22946. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2024. PMID: 38948173 Free PMC article.
-
Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation enhances testicular volume and hemodynamics, reproductive hormones, sperm quality, and seminal antioxidant capacity in goat bucks under summer hot humid conditions.Vet Res Commun. 2022 Dec;46(4):1245-1257. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-09991-8. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Vet Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36048337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar S. R., Devi A. S. Lead toxicity on male reproductive system and its mechanism: a review. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2018;11(3):p. 1228. doi: 10.5958/0974-360x.2018.00228.7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

