Impact of the Renin-Angiotensin System on the Endothelium in Vascular Dementia: Unresolved Issues and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 32560034
- PMCID: PMC7349348
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21124268
Impact of the Renin-Angiotensin System on the Endothelium in Vascular Dementia: Unresolved Issues and Future Perspectives
Erratum in
-
Correction: Noureddine et al. Impact of the Renin-Angiotensin System on the Endothelium in Vascular Dementia: Unresolved Issues and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4268.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 5;25(5):2995. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052995. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474326 Free PMC article.
Abstract
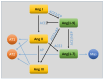
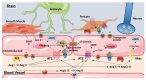
The effects of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) surpass the renal and cardiovascular systems to encompass other body tissues and organs, including the brain. Angiotensin II (Ang II), the most potent mediator of RAS in the brain, contributes to vascular dementia via different mechanisms, including neuronal homeostasis disruption, vascular remodeling, and endothelial dysfunction caused by increased inflammation and oxidative stress. Other RAS components of emerging significance at the level of the blood-brain barrier include angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), Ang(1-7), and the AT2, Mas, and AT4 receptors. The various angiotensin hormones perform complex actions on brain endothelial cells and pericytes through specific receptors that have either detrimental or beneficial actions. Increasing evidence indicates that the ACE2/Ang(1-7)/Mas axis constitutes a protective arm of RAS on the blood-brain barrier. This review provides an update of studies assessing the different effects of angiotensins on cerebral endothelial cells. The involved signaling pathways are presented and help highlight the potential pharmacological targets for the management of cognitive and behavioral dysfunctions associated with vascular dementia.
Keywords: ACE1; ACE2; AT2 receptor; Ang(1–7); Mas receptor; blood–brain barrier.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The vasoprotective axes of the renin-angiotensin system: Physiological relevance and therapeutic implications in cardiovascular, hypertensive and kidney diseases.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Nov;125(Pt A):21-38. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jun 12. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28619367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AHU377+Valsartan (LCZ696) Modulates Renin-Angiotensin System (RAS) in the Cardiac of Female Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Compared With Valsartan.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019 Sep;24(5):450-459. doi: 10.1177/1074248419838503. Epub 2019 Apr 25. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2019. PMID: 31023080
-
Physical Exercise and ACE2-Angiotensin-(1-7)-Mas Receptor Axis of the Renin Angiotensin System.Protein Pept Lett. 2017 Nov 17;24(9):809-816. doi: 10.2174/0929866524666170728151401. Protein Pept Lett. 2017. PMID: 28758593 Review.
-
The renin-angiotensin system in central nervous system tumors and degenerative diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021 Sep 30;26(9):628-642. doi: 10.52586/4972. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2021. PMID: 34590472 Review.
-
Beneficial Effect of Mas Receptor Deficiency on Vascular Cognitive Impairment in the Presence of Angiotensin II Type 2 Receptor.J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Feb 3;7(3):e008121. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.008121. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29431106 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Heart-brain interaction in cardiogenic dementia: pathophysiology and therapeutic potential.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 24;11:1304864. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1304864. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 38327496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Approaching coronavirus disease 2019: Mechanisms of action of repurposed drugs with potential activity against SARS-CoV-2.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;180:114169. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114169. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32710969 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The "Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy" of Endothelial Dysfunction Markers in Human Fertility.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 4;22(5):2584. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052584. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiotensin II increases respiratory rhythmic activity in the preBötzinger complex without inducing astroglial calcium signaling.Front Cell Neurosci. 2023 Feb 2;17:1111263. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1111263. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36816850 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the renin-angiotensin system in the development of COVID-19-associated neurological manifestations.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Sep 16;16:977039. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.977039. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36187294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tarantini S., Tran C.H.T., Gordon G.R., Ungvari Z., Csiszar A. Impaired neurovascular coupling in aging and Alzheimer’s disease: Contribution of astrocyte dysfunction and endothelial impairment to cognitive decline. Exp. Gerontol. 2017;94:52–58. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2016.11.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Csiszar A., Tarantini S., Fülöp G.A., Kiss T., Valcarcel-Ares M.N., Galvan V., Ungvari Z., Yabluchanskiy A. Hypertension impairs neurovascular coupling and promotes microvascular injury: Role in exacerbation of Alzheimer’s disease. Geroscience. 2017;39:359–372. doi: 10.1007/s11357-017-9991-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- #103556/Collaborative Research Stimulus (CRS)
- R01 AG057842/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AG050049/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- Seed grant #100410/Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
- P20 GM104357/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- #103507/103487/Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique
- P20 GM121334/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AG050049, AG057842, P20GM104357, GM104938, P20GM125528/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK104184/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- #2016089/South-Eastern Norway Regional Health Authority
- P20 GM103447/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 16GRNT31200036/American Heart Association
- R01 HL138685/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MPP - 320145/320095/American University of Beirut Faculty of Medicine
- P20 GM125528/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

