Downregulated brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein-1 inhibits osteogenesis of BMSCs through p53 in type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 32554484
- PMCID: PMC7358138
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.051482
Downregulated brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein-1 inhibits osteogenesis of BMSCs through p53 in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Downregulated brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein-1 inhibits osteogenesis of BMSCs through p53 in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Biol Open. 2022 Jun 15;11(6):bio058581. doi: 10.1242/bio.058581. Epub 2022 Jun 28. Biol Open. 2022. PMID: 35762673 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Expression of concern in
-
Expression of Concern: Downregulated brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein-1 inhibits osteogenesis of BMSCs through p53 in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Biol Open. 2020 Oct 5;9(10):bio055525. doi: 10.1242/bio.055525. Biol Open. 2020. PMID: 33020142 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
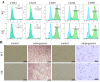
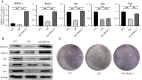
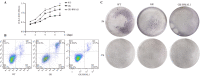
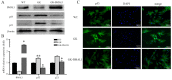
The bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs)-mediated abnormal bone metabolism can delay and impair the bone remodeling process in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Our previous study demonstrated that the downregulation of brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein 1 (BMAL1), a circadian clock protein, inhibited the Wnt/β-catenin pathway via enhanced GSK-3β in diabetic BMSCs. In this article, we confirmed that the downregulated BMAL1 in T2DM played an inhibitory role in osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Upregulation of BMAL1 in the diabetic BMSCs significantly recovered the expression pattern of osteogenic marker genes and alkaline phosphatase (Alp) activity. We also observed an activation of the p53 signaling pathways, exhibited by increased p53 and p21 in diabetic BMSCs. Downregulation of p53 resulting from overexpression of BMAL1 was detected, and when we applied p53 gene silencing (shRNA) and the p53 inhibitor, pifithrin-α (PFT-α), the impaired osteogenic differentiation ability of diabetic BMSCs was greatly restored. However, there was no change in the level of expression of BMAL1. Taken together, our results first revealed that BMAL1 regulated osteogenesis of BMSCs through p53 in T2DM, providing a novel direction for further exploration of the mechanism underlying osteoporosis in diabetes.
Keywords: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs); Brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein-1 (BMAL1); Osteogenic differentiation; Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM); p53.
© 2020. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Brain and muscle aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator-like protein-1 cooperates with glycogen synthase kinase-3β to regulate osteogenesis of bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells in type 2 diabetes.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017 Jan 15;440:93-105. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 4. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27717746
-
BMAL1 regulates balance of osteogenic-osteoclastic function of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in type 2 diabetes mellitus through the NF-κB pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2018 Dec;45(6):1691-1704. doi: 10.1007/s11033-018-4312-7. Epub 2018 Sep 27. Mol Biol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30259246
-
Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by upregulating BMAL1 expression via BMP signaling.Mol Med Rep. 2020 Mar;21(3):1590-1596. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.10954. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Mol Med Rep. 2020. PMID: 32016461 Free PMC article.
-
Bmal1- and Per2-mediated regulation of the osteogenic differentiation and proliferation of mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jun;49(6):4485-4501. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07292-6. Epub 2022 Apr 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35386071
-
[Baduanjin improves sleep quality in patients with type 2 diabetes possibly via regulating Bmal1 gene].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024 Jun 25;76(3):447-456. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38939939 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
miR-21 regulates osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation of BMSCs by targeting PTEN.J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2021 Dec 1;21(4):568-576. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2021. PMID: 34854397 Free PMC article.
-
Role of p53 in promoting BMP9‑induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through TGF‑β1.Exp Ther Med. 2023 Apr 13;25(6):248. doi: 10.3892/etm.2023.11947. eCollection 2023 Jun. Exp Ther Med. 2023. PMID: 37153899 Free PMC article.
-
miR-126 in Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Hepatoblastoma Cells Promotes the Tumorigenesis of Hepatoblastoma through Inducing the Differentiation of BMSCs into Cancer Stem Cells.J Immunol Res. 2021 Oct 29;2021:6744715. doi: 10.1155/2021/6744715. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34746322 Free PMC article.
-
BMAL1 Promotes Valvular Interstitial Cells' Osteogenic Differentiation through NF-κ B/AKT/MAPK Pathway.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023 Mar 6;10(3):110. doi: 10.3390/jcdd10030110. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2023. PMID: 36975874 Free PMC article.
-
miR-155-5p/Bmal1 Modulates the Senescence and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mouse BMSCs through the Hippo Signaling Pathway.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 Feb;20(2):554-567. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10666-3. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024. PMID: 38150082 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown M. L., Yukata K., Farnsworth C. W., Chen D.-G., Awad H., Hilton M. J., O'Keefe R. J., Xing L., Mooney R. A. and Zuscik M. J. (2014). Delayed fracture healing and increased callus adiposity in a C57BL/6J murine model of obesity-associated type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 9, e99656 10.1371/journal.pone.0099656 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Degen R. M., Carbone A., Carballo C., Zong J., Chen T., Lebaschi A., Ying L., Deng X.-H. and Rodeo S. A. (2016). The effect of purified human bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells on rotator cuff tendon healing in an athymic rat. Arthroscopy 32, 2435-2443. 10.1016/j.arthro.2016.04.019 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

