Chronic-plus-binge alcohol intake induces production of proinflammatory mtDNA-enriched extracellular vesicles and steatohepatitis via ASK1/p38MAPKα-dependent mechanisms
- PMID: 32544093
- PMCID: PMC7453887
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.136496
Chronic-plus-binge alcohol intake induces production of proinflammatory mtDNA-enriched extracellular vesicles and steatohepatitis via ASK1/p38MAPKα-dependent mechanisms
Abstract
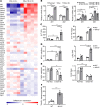
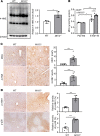
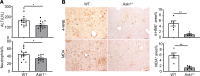
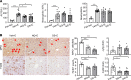
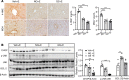
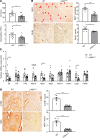
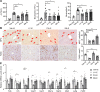
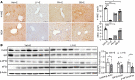
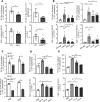
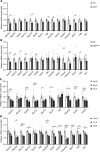
Alcohol-associated liver disease is a spectrum of liver disorders with histopathological changes ranging from simple steatosis to steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Recent data suggest that chronic-plus-binge ethanol intake induces steatohepatitis by promoting release by hepatocytes of proinflammatory mitochondrial DNA-enriched (mtDNA-enriched) extracellular vesicles (EVs). The aim of the present study was to investigate the role of the stress kinase apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38) in chronic-plus-binge ethanol-induced steatohepatitis and mtDNA-enriched EV release. Microarray analysis revealed the greatest hepatic upregulation of metallothionein 1 and 2 (Mt1/2), which encode 2 of the most potent antioxidant proteins. Genetic deletion of the Mt1 and Mt2 genes aggravated ethanol-induced liver injury, as evidenced by elevation of serum ALT, neutrophil infiltration, oxidative stress, and ASK1/p38 activation in the liver. Inhibition or genetic deletion of Ask1 or p38 ameliorated ethanol-induced liver injury, inflammation, ROS levels, and expression of phagocytic oxidase and ER stress markers in the liver. In addition, inhibition of ASK1 or p38 also attenuated ethanol-induced mtDNA-enriched EV secretion from hepatocytes. Taken together, these findings indicate that induction of hepatic mtDNA-enriched EVs by ethanol is dependent on ASK1 and p38, thereby promoting alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Keywords: Hepatology; Toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte-specific deletion of cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 exacerbates alcohol-induced liver injury by activating stress kinases.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 31;18(4):1612-1626. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.67852. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35280676 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative and ER stress-dependent ASK1 activation in steatotic hepatocytes and Kupffer cells sensitizes mice fatty liver to ischemia/reperfusion injury.Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Nov;112:141-148. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.07.020. Epub 2017 Jul 21. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017. PMID: 28739531
-
Fat-Specific Protein 27/CIDEC Promotes Development of Alcoholic Steatohepatitis in Mice and Humans.Gastroenterology. 2015 Oct;149(4):1030-41.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.06.009. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 26099526 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity and binge alcohol intake are deadly combination to induce steatohepatitis: A model of high-fat diet and binge ethanol intake.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;26(4):586-594. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0100. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32937687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation mechanisms of ASK1 in response to various stresses and its significance in intracellular signaling.Adv Biol Regul. 2013 Jan;53(1):135-44. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2012.09.006. Epub 2012 Sep 13. Adv Biol Regul. 2013. PMID: 23031789 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatocyte-specific deletion of cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes 1 exacerbates alcohol-induced liver injury by activating stress kinases.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 31;18(4):1612-1626. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.67852. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35280676 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological Contribution of Extracellular Vesicles and Their MicroRNAs to Progression of Chronic Liver Disease.Biology (Basel). 2022 Apr 21;11(5):637. doi: 10.3390/biology11050637. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35625364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Dynamic Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Chronic Liver Disease.Am J Pathol. 2023 Oct;193(10):1389-1399. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2023.03.009. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Am J Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37028592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of procyanidins on lipid metabolism and inflammation in rats exposed to alcohol and iron.Heliyon. 2020 Sep 7;6(9):e04847. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04847. eCollection 2020 Sep. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 32964156 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of chronic intermittent ethanol vapor exposure on RNA content of brain-derived extracellular vesicles.Alcohol. 2022 Dec;105:9-24. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2022.08.006. Epub 2022 Aug 30. Alcohol. 2022. PMID: 36055466 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

