Quantifying E2F1 protein dynamics in single cells
- PMID: 32542116
- PMCID: PMC7295171
- DOI: 10.1007/s40484-019-0193-6
Quantifying E2F1 protein dynamics in single cells
Abstract
Background: E2F1 protein, a major effector of the Rb/E2F pathway plays a central role in regulating cell-fate decisions involved in proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation. Its expression is highly dynamic and tightly modulated through a combination of transcriptional, translational and posttranslational controls. However, the mechanisms by which its expression and activity can promote different cellular outcomes remain to be fully elucidated. To better document E2F1 expression in live cells, we have engineered a series of fluorescent E2F1 protein reporters that quantitatively capture E2F1 protein dynamics.
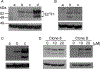
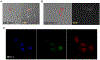
Methods: Reporter constructs, under the control of the mouse or human E2F1 proximal promoter, were designed to express an E2F1-Venus fusion protein incapable of binding DNA. In addition, constructs either included or excluded the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of the E2F1 gene. These constructs were introduced into fibroblasts and epithelial cells, and expression of the fusion reporter protein was validated and quantified in single cells using live imaging.
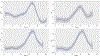
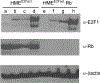
Results: In all cases, expression of the reporter protein effectively recapitulated the behavior of E2F1 under various conditions, including cell cycle progression and genotoxic stress. No or little fluorescent signal of the reporter was detected in G0, but as the cycle progressed, expression of the reporter protein steadily increased in the nucleus, peaking a few hours before cell division, but declining to baseline 2-3 h prior to the onset of mitosis. The absence of the E2F1 3'UTR in the constructs led to considerably higher steady-state levels of the fusion protein, which although normally regulated, exhibited a slightly less complex dynamic profile during the cell cycle or genotoxic stress. Lastly, the presence or absence of Rb failed to impact the overall detection and levels of the reporter proteins.
Conclusions: Our validated E2F1 protein reporters complement nicely other reporters of the Rb/E2F pathway and provide a unique tool to follow the complex dynamics of E2F1 expression in real time in single cells.
Keywords: E2F1 reporter; cell cycle; protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors Bernard Mathey-Prevot, Bao-Tran Parker, Carolyn Im, Cierra Hong, Peng Dong, Guang Yao and Lingchong You declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6) alters E2F1/Rb pathways and utilizes the E2F1 transcription factor to express viral genes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014 Jan 7;111(1):451-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308854110. Epub 2013 Dec 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014. PMID: 24335704 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Rb/E2F pathway results in increased cyclooxygenase-2 expression and activity in prostate epithelial cells.Cancer Res. 2005 May 1;65(9):3633-42. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3129. Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 15867358
-
MyoD activity upregulates E2F1 and enhances transcription from the cyclin E promoter in differentiating myoblasts lacking a functional retinoblastoma protein.Exp Cell Res. 2001 Oct 1;269(2):301-11. doi: 10.1006/excr.2001.5318. Exp Cell Res. 2001. PMID: 11570822
-
Regulation of the G1/S transition phase in mesangial cells by E2F1.Kidney Int. 1999 Oct;56(4):1238-41. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00705.x. Kidney Int. 1999. PMID: 10504464 Review.
-
E2F1: Cause and Consequence of DNA Replication Stress.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Feb 16;7:599332. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.599332. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33665206 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Post-Translational Acetylation and Deacetylation of Signaling Proteins and Transcription Factors after Cerebral Ischemia: Facts and Hypotheses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 26;22(15):7947. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157947. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360712 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
