Clinical characteristics of 182 pediatric COVID-19 patients with different severities and allergic status
- PMID: 32524611
- PMCID: PMC7307120
- DOI: 10.1111/all.14452
Clinical characteristics of 182 pediatric COVID-19 patients with different severities and allergic status
Abstract
Background: The pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection has made widespread impact recently. We aim to investigate the clinical characteristics of COVID-19 children with different severities and allergic status.
Methods: Data extracted from the electronic medical records, including demographics, clinical manifestations, comorbidities, laboratory and immunological results, and radiological images of 182 hospitalized COVID-19 children, were summarized and analyzed.
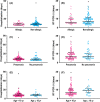
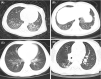
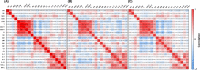
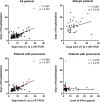
Results: The median age was 6 years, ranging from 3 days to 15 years, and there were more boys (male-female ratio about 2:1) within the studied 182 patients. Most of the children were infected by family members. Fever (43.4%) and dry cough (44.5%) were common symptoms, and gastrointestinal manifestations accounted for 11.0%, including diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, and vomiting. 71.4% had abnormal chest computed tomography (CT) scan images, and typical signs of pneumonia were ground-glass opacity and local patchy shadowing on admission. Laboratory results were mostly within normal ranges, and only a small ratio of lymphopenia (3.9%) and eosinopenia (29.5%) were observed. The majority (97.8%) of infected children were not severe, and 24 (13.2%) of them had asymptomatic infections. Compared to children without pneumonia (manifested as asymptomatic and acute upper respiratory infection), children with pneumonia were associated with higher percentages of the comorbidity history, symptoms of fever and cough, and increased levels of serum procalcitonin, alkaline phosphatase, and serum interleukins (IL)-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α. There were no differences in treatments, duration of hospitalization, time from first positive to first negative nucleic acid testing, and outcomes between children with mild pneumonia and without pneumonia. All the hospitalized COVID-19 children had recovered except one death due to intussusception and sepsis. In 43 allergic children with COVID-19, allergic rhinitis (83.7%) was the major disease, followed by drug allergy, atopic dermatitis, food allergy, and asthma. Demographics and clinical features were not significantly different between allergic and nonallergic groups. Allergic patients showed less increase in acute phase reactants, procalcitonin, D-dimer, and aspartate aminotransferase levels compared with all patients. Immunological profiles including circulating T, B, and NK lymphocyte subsets, total immunoglobulin and complement levels, and serum cytokines did not show any difference in allergic and pneumonia groups. Neither eosinophil counts nor serum total immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels showed a significant correlation with other immunological measures, such as other immunoglobulins, complements, lymphocyte subset numbers, and serum cytokine levels.
Conclusion: Pediatric COVID-19 patients tended to have a mild clinical course. Patients with pneumonia had higher proportion of fever and cough and increased inflammatory biomarkers than those without pneumonia. There was no difference between allergic and nonallergic COVID-19 children in disease incidence, clinical features, and laboratory and immunological findings. Allergy was not a risk factor for developing and severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection and hardly influenced the disease course of COVID-19 in children.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; allergy; children; lymphocyte subsets; pneumonia.
© 2020 EAACI and John Wiley and Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley and Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Akdis reports grants from Allergopharma, Idorsia, Swiss National Science Foundation, Christine Kühne‐Center for Allergy Research and Education, European Commission's Horizon 2020 Framework Programme, Cure, Novartis Research Institutes, Astra Zeneca, and Scibase, and for advisory role in Sanofi/Regeneron, outside the submitted work. Dr Cao, Dr Li, Dr Liu, Dr Chen, Dr Du, Dr Zhang, Prof. Akdis M, Dr Huang, Dr Dong, Dr Lu, and Dr Gao have nothing to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China.Allergy. 2020 Jul;75(7):1730-1741. doi: 10.1111/all.14238. Epub 2020 Feb 27. Allergy. 2020. PMID: 32077115
-
Viral loads, lymphocyte subsets and cytokines in asymptomatic, mildly and critical symptomatic patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a retrospective study.Virol J. 2021 Jun 12;18(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01597-x. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 34118952 Free PMC article.
-
Pediatric COVID-19: Systematic review of the literature.Am J Otolaryngol. 2020 Sep-Oct;41(5):102573. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102573. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Am J Otolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 32531620 Free PMC article.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
-
Systematic Review: Clinical Symptoms and Laboratory and Radiology Findings in Children with COVID-19.Niger J Clin Pract. 2021 Sep;24(9):1259-1267. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_577_20. Niger J Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34531335 Review.
Cited by
-
The outcomes of COVID-19 and acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jan 4;9:6. doi: 10.21037/tgh-23-58. eCollection 2024. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38317749 Free PMC article.
-
Children and young adults hospitalized for severe COVID-19 exhibit thrombotic coagulopathy.Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2021 Jul;68(7):e28975. doi: 10.1002/pbc.28975. Epub 2021 Mar 4. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33661561 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus global pandemic: An overview of current findings among pediatric patients.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020 Dec;55(12):3252-3267. doi: 10.1002/ppul.25087. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2020. PMID: 32965785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 in a group of children with asthma: presentation, severity, and outcome.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 Dec 15;11(6):92-102. eCollection 2022. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36660141 Free PMC article.
-
Mild and Asymptomatic Coronavirus Disease in Children, Adolescents, and Household Contacts and Prolonged Viral Excretion.Int J Microbiol. 2022 Jul 5;2022:5625104. doi: 10.1155/2022/5625104. eCollection 2022. Int J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35813120 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wuhan Municipal Health Commission . Report of clustering pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan City, 2019.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) . Responding to community spread of COVID‐19 (Interim guidance) 7 March 2020. https://www.who.int/publications‐detail/responding‐to‐community‐spread‐o... Accessed April 23, 2020.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

