The Migratory Properties and Numbers of T Regulatory Cell Subsets in Circulation Are Differentially Influenced by Season and Are Associated With Vitamin D Status
- PMID: 32508805
- PMCID: PMC7248210
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00685
The Migratory Properties and Numbers of T Regulatory Cell Subsets in Circulation Are Differentially Influenced by Season and Are Associated With Vitamin D Status
Abstract
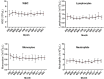
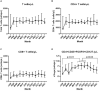
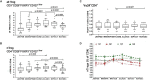
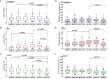
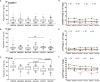
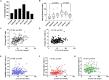
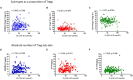
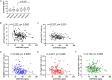
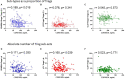
The control of peripheral immune responses by FOXP3+ T regulatory (Treg) cells is essential for immune tolerance. However, at any given time, Treg frequencies in whole blood can vary more than fivefold between individuals. An understanding of factors that influence Treg numbers and migration within and between individuals would be a powerful tool for cellular therapies that utilize the immunomodulatory properties of Tregs to control pathology associated with inflammation. We sought to understand how season could influence Treg numbers and phenotype by monitoring the proportion of natural thymus-derived Tregs (nTregs) defined as (CD3+CD4+CD25+FOXP3+CD127-/low ) cells as a proportion of CD4+ T cells and compared these to all FOXP3+ Tregs (allTregs, CD3+CD25+FOXP3+CD127-/low ). We were able to determine changes within individuals during 1 year suggesting an influence of season on nTreg frequencies. We found that, between individuals at any given time, nTreg/CD4+ T cells ranged from 1.8% in February to 8.8% in the summer where median nTreg/CD4 in January and February was 2.4% (range 3.75-1.76) and in July and August was 4.5% (range 8.81-3.17) p = 0.025. Importantly we were able to monitor individual nTreg frequencies throughout the year in donors that started the year with high or low nTregs. Some nTreg variation could be attributed to vitamin D status where normal linear regression estimated that an absolute increase in nTreg/CD4+ by 0.11% could be expected with 10 nmol increase in serum 25 (OH) vitamin D3 (p = 0.005, 95% CI: 0.03-0.19). We assessed migration markers on Tregs for the skin and/or gut. Here cutaneous lymphocyte associated antigen (CLA+) expression on CD25+FOXP3+CD4+/CD4+ was compared with the same population expressing the gut associated integrin, β7. Gut tropic CD25+FOXP3+β7+Tregs/CD4+ had similar dynamics to nTreg/CD4+. Conversely, CD25+FOXP3+CLA+Tregs/CD4+ showed no association with vitamin D status. Important for cellular therapies requiring isolation of Tregs, the absolute number of β7+CD4+CD25+FOXP3+Tregs was positively associated with 25(OH)vitamin D3 (R2 = 0.0208, r = 0.184, p = 0.021) whereas the absolute numbers of CLA+CD4+CD25+FOXP3+Tregs in the periphery were not influenced by vitamin D status. These baseline observations provide new opportunities to utilize seasonal variables that influence Treg numbers and their migratory potential in patients or donors.
Keywords: Tregs; migration; regulatory T cells; seasons; tolerance; vitamin D3.
Copyright © 2020 Lamikanra, Tsang, Elsiddig, Spencer, Curnow, Danby and Roberts.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low utility of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in predicting peripheral Treg and Th17 cell counts in ESRD and renal transplant patients.Transpl Immunol. 2017 Aug;43-44:3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Transpl Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28757397 Clinical Trial.
-
CD4+CD25+CD127-Foxp3+ and CD8+CD28- Tregs in Renal Transplant Recipients: Phenotypic Patterns, Association With Immunosuppressive Drugs, and Interaction With Effector CD8+ T Cells and CD19+IL-10+ Bregs.Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 15;12:716559. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.716559. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34335631 Free PMC article.
-
The Proportion of Regulatory T Cells in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis: A Meta-Analysis.J Immunol Res. 2019 Oct 23;2019:1058738. doi: 10.1155/2019/1058738. eCollection 2019. J Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31772947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of the season on vitamin D levels and regulatory T cells in patients with polymorphic light eruption.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2016 Mar;15(3):440-6. doi: 10.1039/c5pp00398a. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2016. PMID: 26911519 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Beyond FOXP3: a 20-year journey unravelling human regulatory T-cell heterogeneity.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 12;14:1321228. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1321228. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38283365 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The contribution of thymic tolerance to central nervous system autoimmunity.Semin Immunopathol. 2021 Feb;43(1):135-157. doi: 10.1007/s00281-020-00822-z. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Semin Immunopathol. 2021. PMID: 33108502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Contrasting Seasonality Patterns of Some Cancer-Types and Herpes Zoster Can Be Explained by a Binary Classification of Immunological Reactions.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Dec 15;15:6761-6771. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S392082. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36544697 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

