High dynamism for neo-sex chromosomes: satellite DNAs reveal complex evolution in a grasshopper
- PMID: 32499661
- PMCID: PMC7426270
- DOI: 10.1038/s41437-020-0327-7
High dynamism for neo-sex chromosomes: satellite DNAs reveal complex evolution in a grasshopper
Abstract
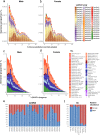
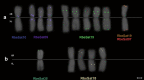
A common characteristic of sex chromosomes is the accumulation of repetitive DNA, which accounts for their diversification and degeneration. In grasshoppers, the X0 sex-determining system in males is considered ancestral. However, in some species, derived variants like neo-XY in males evolved several times independently by Robertsonian translocation. This is the case of Ronderosia bergii, in which further large pericentromeric inversion in the neo-Y also took place, making this species particularly interesting for investigating sex chromosome evolution. Here, we characterized the satellite DNAs (satDNAs) and transposable elements (TEs) of the species to investigate the quantitative differences in repeat composition between male and female genomes putatively associated with sex chromosomes. We found a total of 53 satDNA families and 56 families of TEs. The satDNAs were 13.5% more abundant in males than in females, while TEs were just 1.02% more abundant in females. These results imply differential amplification of satDNAs on neo-Y chromosome and a minor role of TEs in sex chromosome differentiation. We showed highly differentiated neo-XY sex chromosomes owing to major amplification of satDNAs in neo-Y. Furthermore, chromosomal mapping of satDNAs suggests high turnover of neo-sex chromosomes in R. bergii at the intrapopulation level, caused by multiple paracentric inversions, amplifications, and transpositions. Finally, the species is an example of the action of repetitive DNAs in the generation of variability for sex chromosomes after the suppression of recombination, and helps understand sex chromosome evolution at the intrapopulation level.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Uncovering the evolutionary history of neo-XY sex chromosomes in the grasshopper Ronderosia bergii (Orthoptera, Melanoplinae) through satellite DNA analysis.BMC Evol Biol. 2018 Jan 8;18(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s12862-017-1113-x. BMC Evol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29329524 Free PMC article.
-
Tracking the evolution of sex chromosome systems in Melanoplinae grasshoppers through chromosomal mapping of repetitive DNA sequences.BMC Evol Biol. 2013 Aug 9;13:167. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-13-167. BMC Evol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23937327 Free PMC article.
-
Neo-sex chromosomes of Ronderosia bergi: insight into the evolution of sex chromosomes in grasshoppers.Chromosoma. 2015 Sep;124(3):353-65. doi: 10.1007/s00412-015-0505-1. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Chromosoma. 2015. PMID: 25605041
-
[Role of transposons in origin and evolution of plant XY sex chromosomes].Yi Chuan. 2015 Feb;37(2):157-164. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.14-305. Yi Chuan. 2015. PMID: 25665642 Review. Chinese.
-
Decoding the Role of Satellite DNA in Genome Architecture and Plasticity-An Evolutionary and Clinical Affair.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 9;11(1):72. doi: 10.3390/genes11010072. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31936645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Repetitive DNA Elements on Snake Genome Biology and Evolution.Cells. 2021 Jul 6;10(7):1707. doi: 10.3390/cells10071707. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Transposable Elements in Genus Calliptamus Grasshoppers Revealed That Satellite DNA Contributes to Genome Size Variation.Insects. 2021 Sep 17;12(9):837. doi: 10.3390/insects12090837. Insects. 2021. PMID: 34564277 Free PMC article.
-
Large vs small genomes in Passiflora: the influence of the mobilome and the satellitome.Planta. 2021 Apr 1;253(4):86. doi: 10.1007/s00425-021-03598-0. Planta. 2021. PMID: 33792791
-
Comprehensive analysis of the Xya riparia genome uncovers the dominance of DNA transposons, LTR/Gypsy elements, and their evolutionary dynamics.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 12;25(1):687. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10596-5. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38997681 Free PMC article.
-
Satellite DNAs and the evolution of the multiple X1X2Y sex chromosomes in the wolf fish Hoplias malabaricus (Teleostei; Characiformes).Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 2;14(1):20402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70920-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39223262 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acosta MJ, Marchal JA, Martínez S, Puerma E, Bullejos M, de la Guardia RD, et al. Characterization of the satellite DNA Msat-160 from the species Chionomys nivalis (Rodentia, Arvicolinae) Genetica. 2007;130:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Bachtrog D, Kirkpatrick M, Mank JE, McDaniel SF, Pires CJ, Rice W, et al. Are all sex chromosomes created equal? Trends Genet. 2011;27:350–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

