Unveiling functional motions based on point mutations in biased signaling systems: A normal mode study on nerve growth factor bound to TrkA
- PMID: 32497034
- PMCID: PMC7272051
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231542
Unveiling functional motions based on point mutations in biased signaling systems: A normal mode study on nerve growth factor bound to TrkA
Abstract
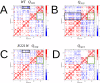
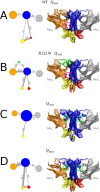
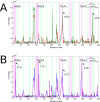
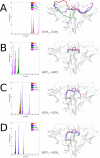
Many receptors elicit signal transduction by activating multiple intracellular pathways. This transduction can be triggered by a non-specific ligand, which simultaneously activates all the signaling pathways of the receptors. However, the binding of one biased ligand preferentially trigger one pathway over another, in a process called biased signaling. The identification the functional motions related to each of these distinct pathways has a direct impact on the development of new effective and specific drugs. We show here how to detect specific functional motions by considering the case of the NGF/TrkA-Ig2 complex. NGF-mediated TrkA receptor activation is dependent on specific structural motions that trigger the neuronal growth, development, and survival of neurons in nervous system. The R221W mutation in the ngf gene impairs nociceptive signaling. We discuss how the large-scale structural effects of this mutation lead to the suppression of collective motions necessary to induce TrkA activation of nociceptive signaling. Our results suggest that subtle changes in the NGF interaction network due to the point mutation are sufficient to inhibit the motions of TrkA receptors putatively linked to nociception. The methodological approach presented in this article, based jointly on the normal mode analysis and the experimentally observed functional alterations due to point mutations provides an essential tool to reveal the structural changes and motions linked to the disease, which in turn could be necessary for a drug design study.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nerve growth factor survival signaling in cultured hippocampal neurons is mediated through TrkA and requires the common neurotrophin receptor P75.Neuroscience. 2002;115(4):1089-108. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00539-0. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12453482
-
Structural and mechanistic insights into nerve growth factor interactions with the TrkA and p75 receptors.Neuron. 2007 Jan 4;53(1):25-38. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.09.034. Neuron. 2007. PMID: 17196528
-
Nerve growth factor: structure and function.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001 May;58(5-6):748-59. doi: 10.1007/pl00000898. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2001. PMID: 11437236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogenesis and function of the NGF/TrkA signaling endosome.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015;314:239-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2014.10.002. Epub 2014 Nov 18. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25619719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optical Activation of TrkA Signaling.ACS Synth Biol. 2018 Jul 20;7(7):1685-1693. doi: 10.1021/acssynbio.8b00126. Epub 2018 Jul 12. ACS Synth Biol. 2018. PMID: 29975841 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
HARP: a database of structural impacts of systematic missense mutations in drug targets of Mycobacterium leprae.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Nov 19;18:3692-3704. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.11.013. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33304465 Free PMC article.
-
Sampling of Protein Conformational Space Using Hybrid Simulations: A Critical Assessment of Recent Methods.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 4;9:832847. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.832847. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35187088 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling mutation effects on the structural dynamics of the main protease from SARS-CoV-2 with hybrid simulation methods.J Mol Graph Model. 2023 Jun;121:108443. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2023.108443. Epub 2023 Feb 22. J Mol Graph Model. 2023. PMID: 36870228 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

