Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: a challenge for cancer therapy
- PMID: 32493414
- PMCID: PMC7268628
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-00904-3
Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: a challenge for cancer therapy
Abstract
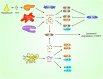
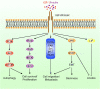
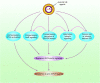
Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) play important roles in mammalian growth, development, aging, and diseases. Aberrant IGFs signaling may lead to malignant transformation and tumor progression, thus providing the rationale for targeting IGF axis in cancer. However, clinical trials of the type I IGF receptor (IGF-IR)-targeted agents have been largely disappointing. Accumulating evidence demonstrates that the IGF axis not only promotes tumorigenesis, but also confers resistance to standard treatments. Furthermore, there are diverse pathways leading to the resistance to IGF-IR-targeted therapy. Recent studies characterizing the complex IGFs signaling in cancer have raised hope to refine the strategies for targeting the IGF axis. This review highlights the biological activities of IGF-IR signaling in cancer and the contribution of IGF-IR to cytotoxic, endocrine, and molecular targeted therapies resistance. Moreover, we update the diverse mechanisms underlying resistance to IGF-IR-targeted agents and discuss the strategies for future development of the IGF axis-targeted agents.
Keywords: Cancer; Drug resistance; Insulin-like growth factor; Receptor tyrosine kinase; Tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Advances in targeting insulin-like growth factor signaling pathway in cancer treatment.Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(17):2899-911. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990595. Curr Pharm Des. 2014. PMID: 23944362 Review.
-
Plasma and tissue insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) as a prognostic marker for prostate cancer and anti-IGF-IR agents as novel therapeutic strategy for refractory cases: a review.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011 Sep 15;344(1-2):1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2011.07.002. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011. PMID: 21782884 Review.
-
IGF-IR signaling in epithelial to mesenchymal transition and targeting IGF-IR therapy: overview and new insights.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jan 30;16(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12943-016-0576-5. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28137302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) in breast cancer: biology and treatment strategies.Tumour Biol. 2016 Sep;37(9):11711-11721. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5176-x. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27444280 Review.
-
Control of apoptosis in human multiple myeloma by insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I).Adv Cancer Res. 2007;97:139-65. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(06)97006-7. Adv Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17419944 Review.
Cited by
-
Blockade of AMPK-Mediated cAMP-PKA-CREB/ATF1 Signaling Synergizes with Aspirin to Inhibit Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 6;13(7):1738. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071738. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33917483 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying dietary acid load in U.S. cancer survivors: an exploratory study using NHANES data.BMC Nutr. 2022 May 3;8(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s40795-022-00537-4. BMC Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35505426 Free PMC article.
-
Triple-negative Breast Cancer: Identification of circRNAs With Efficacy in Preclinical In Vivo Models.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023 Mar-Apr;20(2):117-131. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20368. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 36870692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between circRNAs and miR-141 in Cancer: From Pathogenesis to Diagnosis and Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 24;24(14):11861. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411861. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergism of Carbamoylated Erythropoietin and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in Immediate Early Gene Expression.Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 29;13(9):1826. doi: 10.3390/life13091826. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763230 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

