Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Modulates the Kinetic Profile of the Inflammatory Response of Markers for Neuronal Damage
- PMID: 32492963
- PMCID: PMC7356222
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9061667
Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Modulates the Kinetic Profile of the Inflammatory Response of Markers for Neuronal Damage
Abstract
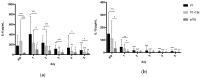
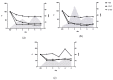
The inflammatory response plays an important role in the pathophysiology of multiple injuries. This study examines the effects of severe trauma and inflammatory response on markers of neuronal damage. A retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data in 445 trauma patients (Injury Severity Score (ISS) ≥ 16) is provided. Levels of neuronal biomarkers (calcium-binding Protein B (S100b), Enolase2 (NSE), glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)) and Interleukins (IL-6, IL-10) in severely injured patients (with polytrauma (PT)) without traumatic brain injury (TBI) or with severe TBI (PT+TBI) and patients with isolated TBI (isTBI) were measured upon arrival until day 5. S100b, NSE, GFAP levels showed a time-dependent decrease in all cohorts. Their expression was higher after multiple injuries (p = 0.038) comparing isTBI. Positive correlation of marker level after concomitant TBI and isTBI (p = 0.001) was noted, while marker expression after PT appears to be independent. Highest levels of IL-6 and -10 were associated to PT und lowest to isTBI (p < 0.001). In all groups pro-inflammatory response (IL-6/-10 ratio) peaked on day 2 and at a lower level on day 4. Severe TBI modulates kinetic profile of inflammatory response by reducing interleukin expression following trauma. Potential markers for neuronal damage have a limited diagnostic value after severe trauma because undifferentiated increase.
Keywords: GFAP; IL-10; IL-6; NSE; S100b; biomarker; multiple trauma; posttraumatic inflammation; risk prediction; traumatic brain injury (TBI).
Conflict of interest statement
C. R. Schindler, T. Lustenberger, M. Woschek, P. Störmann, D. Henrich, P. Radermacher, I. Marzi declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
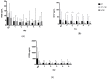
Similar articles
-
miR-142-3p Expression Is Predictive for Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) in Trauma Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5381. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155381. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751105 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of brain injury on the inflammatory response following severe trauma.Immunobiology. 2016 Mar;221(3):427-31. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2015.11.011. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Immunobiology. 2016. PMID: 26688509
-
Admission S100B fails as neuro-marker but is a good predictor for intrahospital mortality in major trauma patients.Injury. 2024 Jan;55(1):111187. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2023.111187. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Injury. 2024. PMID: 37980176
-
Glial and neuronal proteins in serum predict outcome after severe traumatic brain injury.Neurology. 2004 Apr 27;62(8):1303-10. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000120550.00643.dc. Neurology. 2004. PMID: 15111666
-
Systematic Review of Serum Biomarkers in Traumatic Brain Injury.Cureus. 2021 Aug 10;13(8):e17056. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17056. eCollection 2021 Aug. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34522534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Focus on challenges and advances in the treatment of traumatic brain injury.Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024 Aug;50(4):1185-1186. doi: 10.1007/s00068-024-02623-7. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2024. PMID: 39292240 No abstract available.
-
Health Economic Challenge: Geriatric Trauma-An Age-Based Observational Analysis of Treatment Costs and Reimbursement Issues.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jul 6;19(14):8270. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19148270. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35886122 Free PMC article.
-
2D <em>vs</em> 3D morphological analysis of dorsal root ganglia in health and painful neuropathy.Eur J Histochem. 2021 Oct 19;65(s1):3276. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2021.3276. Eur J Histochem. 2021. PMID: 34664808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic and cerebro-cardiac biomarkers following traumatic brain injury: an interim analysis of randomized controlled clinical trial of early administration of beta blockers.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 23;14(1):19574. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70470-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39179700 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Histological and immunohistochemical study of brain damage in traumatic brain injuries in children, depending on the survival period.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2022 Jan-Mar;63(1):169-179. doi: 10.47162/RJME.63.1.18. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2022. PMID: 36074681 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bäckström D., Larsen R., Steinvall I., Fredrikson M., Gedeborg R., Sjöberg F. Deaths caused by injury among people of working age (18–64) are decreasing, while those among older people (64+) are increasing. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2018;44:589–596. doi: 10.1007/s00068-017-0827-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Störmann P., Wagner N., Köhler K., Auner B., Simon T.-P., Pfeifer R., Horst K., Pape H.-C., Hildebrand F., Wutzler S., et al. Monotrauma is associated with enhanced remote inflammatory response and organ damage, while polytrauma intensifies both in porcine trauma model. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2020;46:31–42. doi: 10.1007/s00068-019-01098-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

