Urine cell cycle arrest biomarkers distinguish poorly between transient and persistent AKI in early septic shock: a prospective, multicenter study
- PMID: 32487237
- PMCID: PMC7268340
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-02984-6
Urine cell cycle arrest biomarkers distinguish poorly between transient and persistent AKI in early septic shock: a prospective, multicenter study
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Urine cell cycle arrest biomarkers distinguish poorly between transient and persistent AKI in early septic shock: a prospective, multicenter study.Crit Care. 2020 Aug 4;24(1):483. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03205-w. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32753066 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: The urine biomarkers tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) have been validated for predicting and stratifying AKI. In this study, we analyzed the utility of these biomarkers for distinguishing between transient and persistent AKI in the early phase of septic shock.
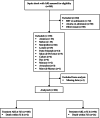
Methods: We performed a prospective, multicenter study in 11 French ICUs. Patients presenting septic shock, with the development of AKI within the first 6 h, were included. Urine [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] was determined at inclusion (0 h), 6 h, 12 h, and 24 h. AKI was considered transient if it resolved within 3 days. Discriminative power was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
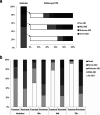
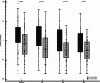
Results: We included 184 patients, within a median [IQR] time of 1.0 [0.0-3.0] h after norepinephrine (NE) initiation; 100 (54%) patients presented transient and 84 (46%) presented persistent AKI. Median [IQR] baseline urine [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] was higher in the persistent AKI group (2.21 [0.81-4.90] (ng/ml)2/1000) than in the transient AKI group (0.75 [0.20-2.12] (ng/ml)2/1000; p < 0.001). Baseline urine [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] was poorly discriminant, with an AUROC [95% CI] of 0.67 [0.59-0.73]. The clinical prediction model combining baseline serum creatinine concentration, baseline urine output, baseline NE dose, and baseline extrarenal SOFA performed well for the prediction of persistent AKI, with an AUROC [95% CI] of 0.81 [0.74-0.86]. The addition of urine [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] to this model did not improve the predictive performance.
Conclusions: Urine [TIMP-2]*[IGFBP7] measurements in the early phase of septic shock discriminate poorly between transient and persistent AKI and do not improve clinical prediction over that achieved with the usual variables.
Trial registration: NCT02812784.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Biomarkers; Recovery; Septic shock.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The urine biomarkers TIMP2 and IGFBP7 can identify patients who will experience severe acute kidney injury following a cardiac arrest: A prospective multicentre study.Resuscitation. 2019 Aug;141:104-110. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2019.06.008. Epub 2019 Jun 16. Resuscitation. 2019. PMID: 31216431
-
Urinary TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 as early biomarkers of acute kidney injury and renal recovery following cardiac surgery.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 27;9(3):e93460. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0093460. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24675717 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of Renal Stress/Damage and Filtration Biomarkers with Subsequent AKI during Hospitalization among Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016 Jun 6;11(6):938-946. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10551015. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27026519 Free PMC article.
-
Current understanding and future directions in the application of TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 in AKI clinical practice.Clin Chem Lab Med. 2019 Apr 24;57(5):567-576. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2018-0776. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2019. PMID: 30179848 Review.
-
Diagnostic value of urinary tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 7 for acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2017 Mar 25;21(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1660-y. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28340605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Performance of the renal resistive index and usual clinical indicators in predicting persistent AKI.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):2028-2038. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2147437. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 36384416 Free PMC article.
-
Update on prognosis driven classification of pediatric AKI.Front Pediatr. 2022 Oct 21;10:1039024. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.1039024. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36340722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary cell cycle biomarkers for the prediction of renal non-recovery in patients with septic acute kidney injury: a prospective study.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023 Dec;27(12):1051-1059. doi: 10.1007/s10157-023-02397-z. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37656396
-
suPAR links a dysregulated immune response to tissue inflammation and sepsis-induced acute kidney injury.JCI Insight. 2023 Apr 10;8(7):e165740. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.165740. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37036003 Free PMC article.
-
Correction to: Urine cell cycle arrest biomarkers distinguish poorly between transient and persistent AKI in early septic shock: a prospective, multicenter study.Crit Care. 2020 Aug 4;24(1):483. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03205-w. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32753066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Peters E, Antonelli M, Wittebole X, Nanchal R, François B, Sakr Y, et al. A worldwide multicentre evaluation of the influence of deterioration or improvement of acute kidney injury on clinical outcome in critically ill patients with and without sepsis at ICU admission: results from the Intensive Care Over Nations audit. Crit Care. 2018;22:188. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2112-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

