Phosphorylation Sites in Protein Kinases and Phosphatases Regulated by Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 Signaling
- PMID: 32471307
- PMCID: PMC7312799
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21113818
Phosphorylation Sites in Protein Kinases and Phosphatases Regulated by Formyl Peptide Receptor 2 Signaling
Abstract
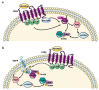
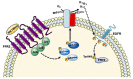
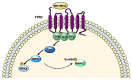
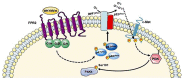
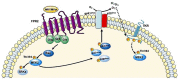
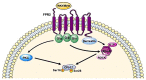
FPR1, FPR2, and FPR3 are members of Formyl Peptides Receptors (FPRs) family belonging to the GPCR superfamily. FPR2 is a low affinity receptor for formyl peptides and it is considered the most promiscuous member of this family. Intracellular signaling cascades triggered by FPRs include the activation of different protein kinases and phosphatase, as well as tyrosine kinase receptors transactivation. Protein kinases and phosphatases act coordinately and any impairment of their activation or regulation represents one of the most common causes of several human diseases. Several phospho-sites has been identified in protein kinases and phosphatases, whose role may be to expand the repertoire of molecular mechanisms of regulation or may be necessary for fine-tuning of switch properties. We previously performed a phospho-proteomic analysis in FPR2-stimulated cells that revealed, among other things, not yet identified phospho-sites on six protein kinases and one protein phosphatase. Herein, we discuss on the selective phosphorylation of Serine/Threonine-protein kinase N2, Serine/Threonine-protein kinase PRP4 homolog, Serine/Threonine-protein kinase MARK2, Serine/Threonine-protein kinase PAK4, Serine/Threonine-protein kinase 10, Dual specificity mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2, and Protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 14A, triggered by FPR2 stimulation. We also describe the putative FPR2-dependent signaling cascades upstream to these specific phospho-sites.
Keywords: FPR2; MAP2K2; MARK2; PAK4; PKN2; PPP1R14A.; PRP4; STK10; cell signaling; phospho-sites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
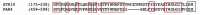
Similar articles
-
Identification of C-terminal phosphorylation sites of N-formyl peptide receptor-1 (FPR1) in human blood neutrophils.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 20;288(38):27042-27058. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.484113. Epub 2013 Jul 19. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23873933 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct signaling cascades elicited by different formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) agonists.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Apr 2;14(4):7193-230. doi: 10.3390/ijms14047193. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23549262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphoproteomic analysis sheds light on intracellular signaling cascades triggered by Formyl-Peptide Receptor 2.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 29;9(1):17894. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-54502-6. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31784636 Free PMC article.
-
N-formyl peptide receptor 3 (FPR3) departs from the homologous FPR2/ALX receptor with regard to the major processes governing chemoattractant receptor regulation, expression at the cell surface, and phosphorylation.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jul 29;286(30):26718-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.244590. Epub 2011 May 4. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21543323 Free PMC article.
-
Formyl peptide receptor 2 is an emerging modulator of inflammation in the liver.Exp Mol Med. 2023 Feb;55(2):325-332. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00941-1. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 36750693 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
β-Arrestin2 Is Critically Involved in the Differential Regulation of Phosphosignaling Pathways by Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone and Taltirelin.Cells. 2022 Apr 27;11(9):1473. doi: 10.3390/cells11091473. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35563779 Free PMC article.
-
Formyl-Peptide Receptor 2 Signaling Modulates SLC7A11/xCT Expression and Activity in Tumor Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;13(5):552. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050552. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790657 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-Resolving FPR2 Agonists Regulate NADPH Oxidase-Dependent Phosphorylation of HSP27, OSR1, and MARCKS and Activation of the Respective Upstream Kinases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jan 19;10(1):134. doi: 10.3390/antiox10010134. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33477989 Free PMC article.
-
Kinase activities in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with prognostic and therapeutic avenues.Mol Oncol. 2024 Aug;18(8):2020-2041. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13625. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Mol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38650175 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand-Based Design of Novel Quinoline Derivatives as Potential Anticancer Agents: An In-Silico Virtual Screening Approach.Molecules. 2024 Jan 15;29(2):426. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020426. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257339 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

