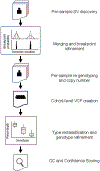
Mapping and characterization of structural variation in 17,795 human genomes
- PMID: 32460305
- PMCID: PMC7547914
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2371-0
Mapping and characterization of structural variation in 17,795 human genomes
Abstract
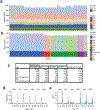
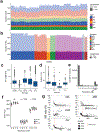
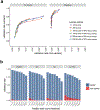
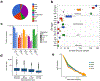
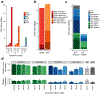
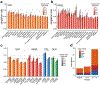
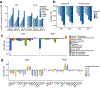
A key goal of whole-genome sequencing for studies of human genetics is to interrogate all forms of variation, including single-nucleotide variants, small insertion or deletion (indel) variants and structural variants. However, tools and resources for the study of structural variants have lagged behind those for smaller variants. Here we used a scalable pipeline1 to map and characterize structural variants in 17,795 deeply sequenced human genomes. We publicly release site-frequency data to create the largest, to our knowledge, whole-genome-sequencing-based structural variant resource so far. On average, individuals carry 2.9 rare structural variants that alter coding regions; these variants affect the dosage or structure of 4.2 genes and account for 4.0-11.2% of rare high-impact coding alleles. Using a computational model, we estimate that structural variants account for 17.2% of rare alleles genome-wide, with predicted deleterious effects that are equivalent to loss-of-function coding alleles; approximately 90% of such structural variants are noncoding deletions (mean 19.1 per genome). We report 158,991 ultra-rare structural variants and show that 2% of individuals carry ultra-rare megabase-scale structural variants, nearly half of which are balanced or complex rearrangements. Finally, we infer the dosage sensitivity of genes and noncoding elements, and reveal trends that relate to element class and conservation. This work will help to guide the analysis and interpretation of structural variants in the era of whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes.Nature. 2012 Nov 1;491(7422):56-65. doi: 10.1038/nature11632. Nature. 2012. PMID: 23128226 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing of Danish Holstein dairy cattle for variant detection and insight into potential loss-of-function variants in protein coding genes.BMC Genomics. 2015 Dec 9;16:1043. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2249-y. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26645365 Free PMC article.
-
svtools: population-scale analysis of structural variation.Bioinformatics. 2019 Nov 1;35(22):4782-4787. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz492. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31218349 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Analysis in the Age of Human Genome Sequencing.Cell. 2019 Mar 21;177(1):70-84. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.02.032. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30901550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular genetic studies of complex phenotypes.Transl Res. 2012 Feb;159(2):64-79. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.08.001. Epub 2011 Aug 31. Transl Res. 2012. PMID: 22243791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-Read Sequencing to Unravel Complex Structural Variants of CEP78 Leading to Cone-Rod Dystrophy and Hearing Loss.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 21;9:664317. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.664317. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33968938 Free PMC article.
-
Misexpression of inactive genes in whole blood is associated with nearby rare structural variants.Am J Hum Genet. 2024 Aug 8;111(8):1524-1543. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.06.017. Epub 2024 Jul 24. Am J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 39053458 Free PMC article.
-
Gamete Binning to Achieve Haplotype-Resolved Genome Assembly.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2590:201-218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2819-5_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36335501
-
Multiple FGF4 Retrocopies Recently Derived within Canids.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jul 23;11(8):839. doi: 10.3390/genes11080839. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32717834 Free PMC article.
-
Monitoring Genomic Structural Rearrangements Resulting from Gene Editing.J Pers Med. 2024 Jan 19;14(1):110. doi: 10.3390/jpm14010110. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 38276232 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007419/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM118335/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG021886/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007416/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG008702/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65236/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65234/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA033619/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG003079/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES015794/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007417/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008895/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG056270/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007376/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65235/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008901/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL135156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65233/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008853/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65237/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AG026395/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG041797/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113315/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128439/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA098758/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL117004/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P60 MD006902/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES024844/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG008898/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK046763/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U24 HG008956/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA136792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007397/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK062431/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- RL5 GM118984/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MD010443/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

