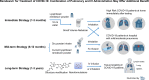
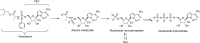Remdesivir for Treatment of COVID-19: Combination of Pulmonary and IV Administration May Offer Aditional Benefit
- PMID: 32458279
- PMCID: PMC7250281
- DOI: 10.1208/s12248-020-00459-8
Remdesivir for Treatment of COVID-19: Combination of Pulmonary and IV Administration May Offer Aditional Benefit
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Remdesivir for Treatment of COVID-19: Combination of Pulmonary and IV Administration May Offer Additional Benefit.AAPS J. 2020 Aug 2;22(5):102. doi: 10.1208/s12248-020-00483-8. AAPS J. 2020. PMID: 32743771 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Remdesivir is one of the most promising drugs to treat COVID-19 based on the following facts: remdesivir has a broad-spectrum antiviral mechanism of action; it demonstrated in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2 and in vivo efficacy in animal models against the similar coronavirus MERS-CoV; its safety profile has been tested in Ebola patients and in compassionate use in COVID-19 patients. Currently, remdesivir is being investigated in ten randomized controlled trials against COVID-19. The dose regimen of remdesivir is an IV loading dose of 200 mg on day 1 followed by daily IV maintenance doses of 100 mg for 5-9 days. Based on our data analysis, however, remdesivir with IV administration alone is unlikely to achieve excellent clinical efficacy. This analysis is based on the following observations: plasma exposures of remdesivir and its active metabolite are unlikely to be correlated with its clinical efficacy; remdesivir and its active metabolites are unlikely to be adequate in the lung to kill the SARS-CoV-2 virus. Even if remdesivir demonstrates benefits in the current randomized controlled trials, its efficacy may be limited. We suggest that a combination of an IV and pulmonary delivery dose regimen should be studied immediately to realize a potentially more effective antiviral therapy against COVID-19. Graphical abstract.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; clinical trials; drug metabolism; pharmacokinetics; pneumonia; pulmonary delivery; remdesivir.
Figures
Comment in
-
Pulmonary administration of remdesivir in the treatment of COVID-19.AAPS J. 2020 Sep 17;22(6):121. doi: 10.1208/s12248-020-00506-4. AAPS J. 2020. PMID: 32944838 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Have we found the panacea to COVID-19 with remdesivir, an old but newly packaged drug?J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2020 Jun;50(2):159-161. doi: 10.4997/JRCPE.2020.217. J R Coll Physicians Edinb. 2020. PMID: 32568289 Review. No abstract available.
-
Audio Interview: New Data on Remdesivir in Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 May 28;382(22):e94. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2019975. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32459948 No abstract available.
-
Remdesivir for the Treatment of COVID-19: A Systematic Review of the Literature.West J Emerg Med. 2020 May 20;21(4):737-741. doi: 10.5811/westjem.2020.5.47658. West J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32726230 Free PMC article.
-
[Remdesivir, the antiviral hope against SARS-CoV-2].Rev Esp Quimioter. 2020 Jun;33(3):176-179. doi: 10.37201/req/028.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 1. Rev Esp Quimioter. 2020. PMID: 32239125 Free PMC article. Review. Spanish.
-
Hepatic Disorders With the Use of Remdesivir for Coronavirus 2019.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Nov;18(12):2835-2836. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.07.050. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32721580 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Remdesivir Discontinuation Decisions Based on Thresholds of Aminotransferase in an Observational Registry.Drugs. 2024 Feb;84(2):209-217. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01981-7. Epub 2024 Jan 10. Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38198063
-
Antiviral attributes of bee venom as a possible therapeutic approach against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Future Virol. 2023 Oct:10.2217/fvl-2023-0127. doi: 10.2217/fvl-2023-0127. Epub 2023 Nov 7. Future Virol. 2023. PMID: 37970095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How to use COVID-19 antiviral drugs in patients with chronic kidney disease.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 9;14:1053814. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1053814. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36843922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 25;1(1):CD014962. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014962.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36695483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Targeting Approach in Selection of Potential Molecule for COVID-19 Treatment.Viruses. 2023 Jan 12;15(1):213. doi: 10.3390/v15010213. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36680253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Wit E, Feldmann F, Cronin J, Jordan R, Okumura A, Thomas T, et al. Prophylactic and therapeutic remdesivir (GS-5734) treatment in the rhesus macaque model of MERS-CoV infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2020;117:6771–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922083117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous