Population Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Relationships of Sarilumab Using Disease Activity Score 28-Joint C-Reactive Protein and Absolute Neutrophil Counts in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
- PMID: 32451909
- PMCID: PMC7658085
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-020-00899-7
Population Pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic Relationships of Sarilumab Using Disease Activity Score 28-Joint C-Reactive Protein and Absolute Neutrophil Counts in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
Background: Sarilumab is a human monoclonal antibody blocking the interleukin-6 receptor alpha (IL-6Rɑ) approved for the treatment of moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis in adults with inadequate response or intolerance to other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs.
Objective: The aim of the current analysis was to describe sarilumab exposure-response relationships.
Methods: Population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PopPK/PD) models were developed describing the time course of the 28-joint disease activity score by C-reactive protein (DAS28-CRP) and absolute neutrophil count (ANC) using data from phase I-III studies (NCT01011959, NCT01061736, NCT01709578, NCT01768572) after subcutaneous sarilumab 50-150 mg every week or 100-200 mg every 2 weeks.
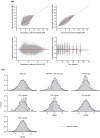
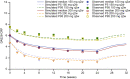
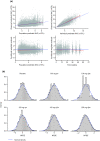
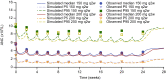
Results: The time course of DAS28-CRP and ANC after sarilumab administration was described by semi-mechanistic, indirect-response models. Drug effect was predicted to be numerically greater at median exposure for the 200 mg every 2 weeks regimen versus the 150 mg every 2 weeks regimen, for both DAS28-CRP (50% vs. 47%) and ANC reduction from baseline (39% vs. 31%), with the latter showing less fluctuations within a dosing interval. Four covariates were retained in the final models: body weight, baseline rheumatoid factor status, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide status, and concomitant methotrexate. There was no clinically meaningful influence of investigated covariates for either model.
Conclusion: The PopPK/PD models showed numerically greater reductions in DAS28-CRP and ANC with sarilumab 200 mg every 2 weeks than with 150 mg every 2 weeks. There was no clinically meaningful influence of investigated covariates. These data contribute to the totality of evidence that supports a sarilumab subcutaneous starting dose of 200 mg every 2 weeks, with a subsequent reduction to 150 mg every 2 weeks in the event of laboratory abnormalities such as neutropenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Christine Xu and Vanaja Kanamaluru are employees of Sanofi Genzyme and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. Lei Ma was an employee of Sanofi Genzyme at the time of this work and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. Anne Paccaly is an employee of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company. None of the authors have any non-financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Subcutaneous Sarilumab and Intravenous Tocilizumab Following Single-Dose Administration in Patients With Active Rheumatoid Arthritis on Stable Methotrexate.J Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;61(1):90-104. doi: 10.1002/jcph.1703. Epub 2020 Jul 29. J Clin Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32726514 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Long-term safety and efficacy of sarilumab plus methotrexate on disease activity, physical function and radiographic progression: 5 years of sarilumab plus methotrexate treatment.RMD Open. 2019 Aug 1;5(2):e000887. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000887. eCollection 2019. RMD Open. 2019. PMID: 31452928 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sarilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody against IL-6Rα in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to methotrexate: efficacy and safety results from the randomised SARIL-RA-MOBILITY Part A trial.Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 Sep;73(9):1626-34. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204405. Epub 2013 Dec 2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014. PMID: 24297381 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sarilumab: Review of a Second IL-6 Receptor Antagonist Indicated for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Ann Pharmacother. 2018 Aug;52(8):780-791. doi: 10.1177/1060028018761599. Epub 2018 Feb 26. Ann Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29482351 Review.
-
Sarilumab: A Review in Moderate to Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis.Drugs. 2018 Jun;78(9):929-940. doi: 10.1007/s40265-018-0929-z. Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29931592 Review.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of Tripterygium wilfordii hook. f. in the treatment of rheumatic and autoimmune diseases: Bioactive compounds, mechanisms of action, and future directions.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 1;14:1282610. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1282610. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38027004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drug dosing in hospitalized obese patients with COVID-19.Crit Care. 2022 Mar 14;26(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-03941-1. Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 35287690 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet. 2018;392:1789–858. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann R, van Adelsberg J, Lin Y, Castelar-Pinheiro GD, Brzezicki J, Hrycaj P, et al. Sarilumab and nonbiologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response or intolerance to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors. Arthr Rheumatol. 2017;69:277–290. doi: 10.1002/art.39944. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Genovese MC, Fleischmann R, Kivitz AJ, Rell-Bakalarska M, Martincova R, Fiore S, et al. Sarilumab plus methotrexate in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis and inadequate response to methotrexate: results of a phase III study. Arthr Rheumatol. 2015;67:1424–1437. doi: 10.1002/art.39093. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Burmester GR, Lin Y, Patel R, van Adelsberg J, Mangan EK, Graham NM, et al. Efficacy and safety of sarilumab monotherapy versus adalimumab monotherapy for the treatment of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis (MONARCH): a randomised, double-blind, parallel-group phase III trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:840–847. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210310. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

