What solid organ transplant healthcare providers should know about renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and COVID-19
- PMID: 32446267
- PMCID: PMC7267091
- DOI: 10.1111/ctr.13991
What solid organ transplant healthcare providers should know about renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and COVID-19
Abstract
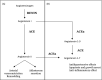
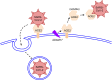
The data on the outcomes of solid organ transplant recipients who have contracted coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are still emerging. Kidney transplant recipients are commonly prescribed renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (AAS) inhibitors given the prevalence of hypertension, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. As the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) facilitates the entry of coronaviruses into target cells, there have been hypotheses that preexisting use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors may increase the risk of developing severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Given the common use of RAAS inhibitors among solid organ transplant recipients, we sought to review the RAAS cascade, the mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 entry, and pertinent data related to the effect of RAAS inhibitors on ACE2 to guide management of solid organ transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic. At present, there is no clear evidence to support the discontinuation of RAAS inhibitors in solid organ transplant recipients during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: ACE2 receptor; COVID-19; renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors; solid organ transplant.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
We have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-SARS-CoV axis: a comprehensive review.Eur Respir J. 2020 Jul 9;56(1):2000912. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00912-2020. Print 2020 Jul. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32341103 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spironolactone may provide protection from SARS-CoV-2: Targeting androgens, angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).Med Hypotheses. 2020 Oct;143:110112. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110112. Epub 2020 Jul 16. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 32721806 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), SARS-CoV-2 and the pathophysiology of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).J Pathol. 2020 Jul;251(3):228-248. doi: 10.1002/path.5471. Epub 2020 Jun 10. J Pathol. 2020. PMID: 32418199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in Coronavirus Infection-Current Considerations During the Pandemic.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020 Jul;34(7):1717-1719. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2020.04.010. Epub 2020 Apr 16. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020. PMID: 32360010 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Circulating plasma concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in men and women with heart failure and effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors.Eur Heart J. 2020 May 14;41(19):1810-1817. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa373. Eur Heart J. 2020. PMID: 32388565 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Attenuated early inflammatory response in solid organ recipients with COVID-19.Clin Transplant. 2020 Oct;34(10):e14027. doi: 10.1111/ctr.14027. Epub 2020 Jul 24. Clin Transplant. 2020. PMID: 32589760 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

