Discovery of novel N-substituted thiazolidinediones (TZDs) as HDAC8 inhibitors: in-silico studies, synthesis, and biological evaluation
- PMID: 32446120
- PMCID: PMC7302971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103934
Discovery of novel N-substituted thiazolidinediones (TZDs) as HDAC8 inhibitors: in-silico studies, synthesis, and biological evaluation
Abstract
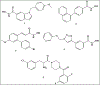
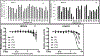
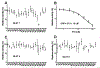
Epigenetics plays a fundamental role in cancer progression, and developing agents that regulate epigenetics is crucial for cancer management. Among Class I and Class II HDACs, HDAC8 is one of the essential epigenetic players in cancer progression. Therefore, we designed, synthesized, purified, and structurally characterized novel compounds containing N-substituted TZD (P1-P25). Cell viability assay of all compounds on leukemic cell lines (CEM, K562, and KCL22) showed the cytotoxic potential of P8, P9, P10, P12, P19, and P25. In-vitro screening of different HDACs isoforms revealed that P19 was the most potent and selective inhibitor for HDAC8 (IC50 - 9.3 μM). Thermal shift analysis (TSA) confirmed the binding of P19 to HDAC8. In-vitro screening of all compounds on the transport activity of GLUT1, GLUT4, and GLUT5 indicated that P19 inhibited GLUT1 (IC50 - 28.2 μM). P10 and P19 induced apoptotic cell death in CEM cells (55.19% and 60.97% respectively) and P19 was less cytotoxic on normal WBCs (CC50 - 104.2 μM) and human fibroblasts (HS27) (CC50 - 105.0 μM). Thus, among this novel series of TZD derivatives, compound P19 was most promising HDAC8 inhibitor and cytotoxic on leukemic cells. Thus, P19 could serve as a lead for further development of optimized molecules with enhanced selectivity and potency.
Keywords: Docking; GLUT; HDAC; Leukemia; N-substituted thiazolidinediones.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest None.
Figures

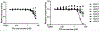
Similar articles
-
Structure guided design and synthesis of furyl thiazolidinedione derivatives as inhibitors of GLUT 1 and GLUT 4, and evaluation of their anti-leukemic potential.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Sep 15;202:112603. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112603. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32634629 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of 5-naphthylidene-2,4-thiazolidinedione derivatives as selective HDAC8 inhibitors and evaluation of their cytotoxic effects in leukemic cell lines.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jan;95:103522. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103522. Epub 2019 Dec 18. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 31901516
-
Discovery of meta-sulfamoyl N-hydroxybenzamides as HDAC8 selective inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Apr 25;150:282-291. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29533873
-
Histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) and its inhibitors with selectivity to other isoforms: An overview.Eur J Med Chem. 2019 Feb 15;164:214-240. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.12.039. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Eur J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 30594678 Review.
-
Selective and nonselective HDAC8 inhibitors: a therapeutic patent review.Pharm Pat Anal. 2018 Nov;7(6):259-276. doi: 10.4155/ppa-2018-0019. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Pharm Pat Anal. 2018. PMID: 30632447 Review.
Cited by
-
Permuted 2,4-thiazolidinedione (TZD) analogs as GLUT inhibitors and their in-vitro evaluation in leukemic cells.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020 Nov 1;154:105512. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2020.105512. Epub 2020 Aug 12. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32801003 Free PMC article.
-
Thiazolidin-2,4-Dione Scaffold: An Insight into Recent Advances as Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Hypoglycemic Agents.Molecules. 2022 Oct 10;27(19):6763. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196763. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-target weapons: diaryl-pyrazoline thiazolidinediones simultaneously targeting VEGFR-2 and HDAC cancer hallmarks.RSC Med Chem. 2021 Jul 27;12(9):1540-1554. doi: 10.1039/d1md00125f. eCollection 2021 Sep 23. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34671737 Free PMC article.
-
2-Aminobenzothiazoles in anticancer drug design and discovery.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Jun;135:106477. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2023.106477. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36989736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of New 2-Phenylamino-3-acyl-1,4-naphthoquinones as Inhibitors of Cancer Cells Proliferation: Searching for Intra-Cellular Targets Playing a Role in Cancer Cells Survival.Molecules. 2023 May 24;28(11):4323. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114323. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298798 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

