Hypoxia-induced GBE1 expression promotes tumor progression through metabolic reprogramming in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 32439898
- PMCID: PMC7242448
- DOI: 10.1038/s41392-020-0152-8
Hypoxia-induced GBE1 expression promotes tumor progression through metabolic reprogramming in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
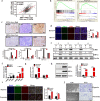
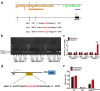
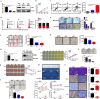
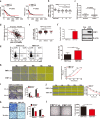
Hypoxia mediates a metabolic switch from oxidative phosphorylation to glycolysis and increases glycogen synthesis. We previously found that glycogen branching enzyme (GBE1) is downstream of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF1) signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cells; however, the molecular mechanism underlying HIF1 regulation of GBE1 expression remains unknown. Herein, the effect of GBE1 on tumor progression via changes in metabolic signaling under hypoxia in vitro and in vivo was evaluated, and GBE1-related genes from human specimens and data sets were analyzed. Hypoxia induced GBE1 upregulation in LUAD cells. GBE1-knockdown A549 cells showed impaired cell proliferation, clone formation, cell migration and invasion, angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis. GBE1 mediated the metabolic reprogramming of LUAD cells. The expression of gluconeogenesis pathway molecules, especially fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBP1), was markedly higher in shGBE1 A549 cells than it was in the control cells. FBP1 inhibited the tumor progression of LUAD. GBE1-mediated FBP1 suppression via promoter methylation enhanced HIF1α levels through NF-κB signaling. GBE1 may be a negative prognostic biomarker for LUAD patients. Altogether, hypoxia-induced HIF1α mediated GBE1 upregulation, suppressing FBP1 expression by promoter methylation via NF-κB signaling in LUAD cells. FBP1 blockade upregulated HIF1α, triggered the switch to anaerobic glycolysis, and enhanced glucose uptake. Therefore, targeting HIF1α/GBE1/NF-κB/FBP1 signaling may be a potential therapeutic strategy for LUAD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Lung adenocarcinoma-intrinsic GBE1 signaling inhibits anti-tumor immunity.Mol Cancer. 2019 Jun 20;18(1):108. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1027-x. Mol Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31221150 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA FAM83A-AS1 facilitates tumor proliferation and the migration via the HIF-1α/ glycolysis axis in lung adenocarcinoma.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Jan 1;18(2):522-535. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.67556. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35002507 Free PMC article.
-
GBE1 Promotes Glioma Progression by Enhancing Aerobic Glycolysis through Inhibition of FBP1.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;15(5):1594. doi: 10.3390/cancers15051594. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900384 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analysis of the hypoxia-related DNA methylation-driven genes in lung adenocarcinoma progression.Biosci Rep. 2020 Feb 28;40(2):BSR20194200. doi: 10.1042/BSR20194200. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32031203 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane progesterone receptor α (mPRα) enhances hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor secretion and angiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma through STAT3 signaling.J Transl Med. 2022 Feb 5;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03270-5. J Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35123491 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Genetics of enzymatic dysfunctions in metabolic disorders and cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Aug 2;13:1230934. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1230934. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37601653 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m6A demethylase FTO promotes tumor progression via regulation of lipid metabolism in esophageal cancer.Cell Biosci. 2022 May 14;12(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13578-022-00798-3. Cell Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35568876 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay Among Metabolism, Epigenetic Modifications, and Gene Expression in Cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Dec 24;9:793428. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.793428. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 35004688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-genome sequencing of copy number variation analysis in Ethiopian cattle reveals adaptations to diverse environments.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 15;25(1):1088. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10936-5. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39548375 Free PMC article.
-
Development of an invasion score based on metastasis-related pathway activity profiles for identifying invasive molecular subtypes of lung adenocarcinoma.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 19;14(1):1692. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-51681-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38243040 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

