Retinoid analogs and polyphenols as potential therapeutics for age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 32438835
- PMCID: PMC7787542
- DOI: 10.1177/1535370220926938
Retinoid analogs and polyphenols as potential therapeutics for age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
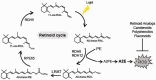
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a devastating retinal degenerative disease. Epidemiological reports showed an expected increasing prevalence of AMD in the near future. The only one existing FDA-approved pharmacological treatment involves an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) therapy with serious disadvantages. This limitation emphasizes an alarming need to develop new therapeutic approaches to prevent and treat AMD. In this review, we summarize scientific data unraveling the therapeutic potential of the specific retinoid and natural compounds. The experimental results reported by us and other research groups demonstrated that retinoid analogs and compounds with natural product scaffolds could serve as lead compounds for the development of new therapeutic agents with potential to prevent or slow down the pathogenesis of AMD.
Keywords: Degeneration; flavonoids; macula; polyphenols; retina; retinoids.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The novel visual cycle inhibitor (±)-RPE65-61 protects retinal photoreceptors from light-induced degeneration.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 13;17(10):e0269437. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269437. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36227868 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of potential therapies for a mouse model of human age-related macular degeneration caused by delayed all-trans-retinal clearance.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009 Oct;50(10):4917-25. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-3581. Epub 2009 Jun 3. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2009. PMID: 19494204 Free PMC article.
-
Prevention and treatment of age-related macular degeneration: an update for pharmacists.Consult Pharm. 2013 Nov;28(11):723-37. doi: 10.4140/TCP.n.2013.723. Consult Pharm. 2013. PMID: 24217192 Review.
-
Natural products for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration.Phytomedicine. 2024 Jul 25;130:155522. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155522. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38820665 Review.
-
[Review and expert opinion in age related macular degeneration. Focus on the pathophysiology, angiogenesis and pharmacological and clinical data].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2014 Sep;37(7):566-79. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2014.06.001. Epub 2014 Sep 1. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2014. PMID: 25190312 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Neuroinflammation as a Therapeutic Target in Retinitis Pigmentosa and Quercetin as Its Potential Modulator.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 16;13(11):1935. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13111935. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34834350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Effects of Flavonoids in Acute Models of Light-Induced Retinal Degeneration.Mol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;99(1):60-77. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.120.000072. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33154094 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of aging, age-associated diseases, and lifespan determination.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Nov;245(17):1529-1531. doi: 10.1177/1535370220955146. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32903037 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bohm MRR, Thanos S. [ The aging retina in the context of cerebral neurodegenerative diseases. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd 2019; 236:682–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

