Isolation and Functions of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Parasites: The Promise of a New Era in Immunotherapy, Vaccination, and Diagnosis
- PMID: 32425527
- PMCID: PMC7196212
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S250993
Isolation and Functions of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Parasites: The Promise of a New Era in Immunotherapy, Vaccination, and Diagnosis
Abstract
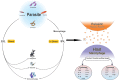
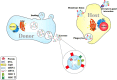
Experimental and epidemiological evidence shows that parasites, particularly helminths, play a central role in balancing the host immunity. It was demonstrated that parasites can modulate immune responses via their excretory/secretory (ES) and some specific proteins. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nano-scale particles that are released from eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. EVs in parasitological studies have been mostly employed for immunotherapy of autoimmune diseases, vaccination, and diagnosis. EVs can carry virulence factors and play a central role in the development of parasites in host cells. These molecules can manipulate the immune responses through transcriptional changes. Moreover, EVs derived from helminths modulate the immune system via provoking anti-inflammatory cytokines. On the other hand, EVs from parasite protozoa can induce efficient immunity, that makes them useful for probable next-generation vaccines. In addition, it seems that EVs from parasites may provide new diagnostic approaches for parasitic infections. In the current study, we reviewed isolation methods, functions, and applications of parasite's EVs in immunotherapy, vaccination, and diagnosis.
Keywords: diagnosis; extracellular vesicles; immunotherapy; parasites; vaccination.
© 2020 Khosravi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest for this work. This study was financially supported by the Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences with grant number: 1029, and received ethical approval from the ethics committee of the university (no. IR.SBMU.RCGLD.REC.1398.015).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Communication Within Host-Parasite Interactions.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 15;9:3066. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03066. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30697211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new level of complexity in parasite-host interaction: The role of extracellular vesicles.Adv Parasitol. 2019;104:39-112. doi: 10.1016/bs.apar.2019.02.003. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Adv Parasitol. 2019. PMID: 31030771 Review.
-
Exosomes and Other Extracellular Vesicles: The New Communicators in Parasite Infections.Trends Parasitol. 2015 Oct;31(10):477-489. doi: 10.1016/j.pt.2015.06.009. Trends Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26433251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Helminth extracellular vesicles: Interactions with the host immune system.Mol Immunol. 2021 Sep;137:124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.06.017. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34246032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of the interaction of helminth extracellular vesicles with the host and their potential functions and biological applications.Mol Immunol. 2021 Jun;134:228-235. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2021.03.020. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Mol Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33836351 Review.
Cited by
-
Helminth Induced Immunoregulation and Novel Therapeutic Avenue of Allergy.J Asthma Allergy. 2020 Oct 7;13:439-451. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S273556. eCollection 2020. J Asthma Allergy. 2020. PMID: 33116652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Trypanosoma cruzi Infection: Immunomodulatory Effects and Future Perspectives as Potential Control Tools against Chagas Disease.J Immunol Res. 2022 Aug 17;2022:5230603. doi: 10.1155/2022/5230603. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 36033396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leishmania 360°: Guidelines for Exosomal Research.Microorganisms. 2021 Oct 2;9(10):2081. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9102081. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34683402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Milk-derived small extracellular vesicles: nanomaterials to promote bone formation.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Aug 11;20(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01580-w. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35953855 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of extracellular vesicles isolated from hydatid cyst fluid and evaluation of immunomodulatory effects on human monocytes.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Sep;27(17):2614-2625. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17894. Epub 2023 Aug 2. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37530547 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

