Rare Genetic Diseases: Nature's Experiments on Human Development
- PMID: 32422592
- PMCID: PMC7229282
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101123
Rare Genetic Diseases: Nature's Experiments on Human Development
Abstract
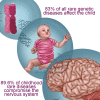
Rare genetic diseases are the result of a continuous forward genetic screen that nature is conducting on humans. Here, we present epistemological and systems biology arguments highlighting the importance of studying these rare genetic diseases. We contend that the expanding catalog of mutations in ∼4,000 genes, which cause ∼6,500 diseases and their annotated phenotypes, offer a wide landscape for discovering fundamental mechanisms required for human development and involved in common diseases. Rare afflictions disproportionately affect the nervous system in children, but paradoxically, the majority of these disease-causing genes are evolutionarily ancient and ubiquitously expressed in human tissues. We propose that the biased prevalence of childhood rare diseases affecting nervous tissue results from the topological complexity of the protein interaction networks formed by ubiquitous and ancient proteins encoded by childhood disease genes. Finally, we illustrate these principles discussing Menkes disease, an example of the discovery power afforded by rare diseases.
Keywords: Clinical Genetics; Human Genetics.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Balancing selection on genomic deletion polymorphisms in humans.Elife. 2023 Jan 10;12:e79111. doi: 10.7554/eLife.79111. Elife. 2023. PMID: 36625544 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating whether nature's intrinsic value is an axiom of or anathema to conservation.Conserv Biol. 2015 Apr;29(2):321-32. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12464. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Conserv Biol. 2015. PMID: 25704250 Review.
-
Prioritization of orphan disease-causing genes using topological feature and GO similarity between proteins in interaction networks.Sci China Life Sci. 2014 Nov;57(11):1064-71. doi: 10.1007/s11427-014-4747-6. Epub 2014 Oct 17. Sci China Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 25326068
-
Ancient DNA analysis of rare genetic bone disorders.Int J Paleopathol. 2021 Jun;33:182-187. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpp.2021.04.009. Epub 2021 May 7. Int J Paleopathol. 2021. PMID: 33971396
-
What Has a Century of Quantitative Genetics Taught Us About Nature's Genetic Tool Kit?Annu Rev Genet. 2020 Nov 23;54:439-464. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-021920-102037. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Annu Rev Genet. 2020. PMID: 32897739 Review.
Cited by
-
FMRP attenuates activity dependent modifications in the mitochondrial proteome.Mol Brain. 2021 Apr 30;14(1):75. doi: 10.1186/s13041-021-00783-w. Mol Brain. 2021. PMID: 33931071 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi-Dependent Copper Homeostasis Sustains Synaptic Development and Mitochondrial Content.J Neurosci. 2021 Jan 13;41(2):215-233. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1284-20.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 18. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33208468 Free PMC article.
-
Burden of rare genetic disorders in India: twenty-two years' experience of a tertiary centre.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Aug 13;19(1):295. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03300-z. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024. PMID: 39138584 Free PMC article.
-
Neurofibromatosis: New Clinical Challenges in the Era of COVID-19.Biomedicines. 2022 Apr 19;10(5):940. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10050940. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Benefits and Challenges of Pediatric-to-Adult Health Care Transition in Childhood-Onset Neurologic Conditions.Neurol Clin Pract. 2023 Apr;13(2):e200130. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000200130. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Neurol Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 37064588 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

