On the polarization of ligands by proteins
- PMID: 32421120
- PMCID: PMC8118567
- DOI: 10.1039/d0cp00376j
On the polarization of ligands by proteins
Abstract
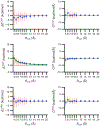
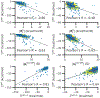
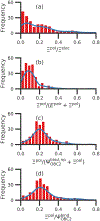
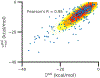
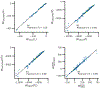
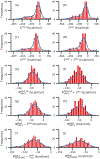
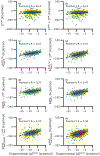
Although ligand-binding sites in many proteins contain a high number density of charged side chains that can polarize small organic molecules and influence binding, the magnitude of this effect has not been studied in many systems. Here, we use a quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) approach, in which the ligand is the QM region, to compute the ligand polarization energy of 286 protein-ligand complexes from the PDBBind Core Set (release 2016). Calculations were performed both with and without implicit solvent based on the domain decomposition Conductor-like Screening Model. We observe that the ligand polarization energy is linearly correlated with the magnitude of the electric field acting on the ligand, the magnitude of the induced dipole moment, and the classical polarization energy. The influence of protein and cation charges on the ligand polarization diminishes with the distance and is below 2 kcal mol-1 at 9 Å and 1 kcal mol-1 at 12 Å. Compared to these embedding field charges, implicit solvent has a relatively minor effect on ligand polarization. Considering both polarization and solvation appears essential to computing negative binding energies in some crystallographic complexes. Solvation, but not polarization, is essential for achieving moderate correlation with experimental binding free energies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
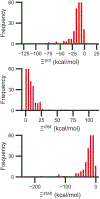
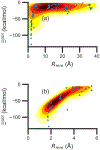
Similar articles
-
Accuracy comparison of several common implicit solvent models and their implementations in the context of protein-ligand binding.J Mol Graph Model. 2017 Mar;72:70-80. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2016.12.011. Epub 2016 Dec 21. J Mol Graph Model. 2017. PMID: 28064081 Free PMC article.
-
Estimates of ligand-binding affinities supported by quantum mechanical methods.Interdiscip Sci. 2010 Mar;2(1):21-37. doi: 10.1007/s12539-010-0083-0. Epub 2010 Jan 28. Interdiscip Sci. 2010. PMID: 20640794
-
Fragment quantum mechanical calculation of proteins and its applications.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Sep 16;47(9):2748-57. doi: 10.1021/ar500077t. Epub 2014 May 22. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24851673
-
Ligand-Binding Affinity Estimates Supported by Quantum-Mechanical Methods.Chem Rev. 2016 May 11;116(9):5520-66. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00630. Epub 2016 Apr 14. Chem Rev. 2016. PMID: 27077817 Review.
-
Prediction of the binding energy for small molecules, peptides and proteins.J Mol Recognit. 1999 May-Jun;12(3):177-90. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-1352(199905/06)12:3<177::AID-JMR451>3.0.CO;2-Z. J Mol Recognit. 1999. PMID: 10398408 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of Family-Specific Features in Cas9 and Cas12 Proteins: A Machine Learning Approach Using Complete Protein Feature Spectrum.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 23:2024.01.22.576286. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.22.576286. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Chem Inf Model. 2024 Jun 24;64(12):4897-4911. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.4c00625. PMID: 38328240 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The future of biomolecular simulation in the pharmaceutical industry: what we can learn from aerodynamics modelling and weather prediction. Part 1. understanding the physical and computational complexity of in silico drug design.Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2021 Nov 1;77(Pt 11):1348-1356. doi: 10.1107/S2059798321009712. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 34726163 Free PMC article.
-
Electrostatics and water occlusion regulate covalently-bound flavin mononucleotide cofactors of Vibrio cholerae respiratory complex NQR.Proteins. 2021 Oct;89(10):1376-1385. doi: 10.1002/prot.26158. Epub 2021 Jun 14. Proteins. 2021. PMID: 34091964 Free PMC article.
-
The therapeutic potential of inorganic polyphosphate: A versatile physiological polymer to control coronavirus disease (COVID-19).Theranostics. 2021 Apr 15;11(13):6193-6213. doi: 10.7150/thno.59535. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 33995653 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Haynes WM, CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 94th Edition, CRC Press, 2016.
-
- Honig B and Nicholls A, Science, 1995, 268, 1144–1149. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Viloca M, Truhlar DG and Gao J, J. Mol. Biol, 2003, 327, 549–560. - PubMed
-
- van der Kamp MW, Perruccio F and Mulholland AJ, Proteins: Struct., Funct., Bioinf, 2007, 69, 521–535. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

