Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Alopecia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan
- PMID: 32411714
- PMCID: PMC7198783
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2020.00150
Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Alopecia: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan
Abstract
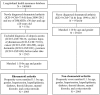
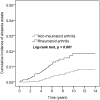
Objectives: Studies on the relationship between rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and alopecia areata (AA) are limited. This study investigated the effect of RA on alopecia areata risk in a nationwide cohort study. Methods: We analyzed 2000-2012 data from the Longitudinal Health Insurance Database in Taiwan. The follow-up period was extended up to the end of 2013. We defined RA as a diagnosis using International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM) code 714.0 during at least three outpatient visits or one admission and the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for >30 days. The enrollees with AA were identified using the ICD-9-CM code 704.01. We enrolled a comparison cohort comprising participants randomly matched by age and sex, with the same index date as that of the study cohort. Furthermore, we investigated alopecia risk by using Cox proportional-hazards regression models after propensity score matching for sex, age, comorbidities, and medication use. Results: In total, 2,905 patients with RA (74% women, mean age: 51.9 years) and 2,905 controls were followed for 22,276 and 25,732 person-years, respectively. Alopecia risk was 2.64-fold (95% confidence interval = 1.47-4.76) higher in patients with RA than in patients without RA after age, sex, comorbidities, and medication use were adjusted for. In addition, patients with thyroid disease presented considerable alopecia risk. Patients with RA in the younger age group (20-40 years) had the highest alopecia risk. Conclusions: Alopecia risk is significantly higher in patients with RA than in those without RA, particularly in the younger age group (20-40 years). RA assessment should be considered when examining patients with alopecia, especially young adults.
Keywords: alopecia; cohort study; corticosteroids; disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2020 Chang, Lee, Leong, Wang and Wei.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Economic Burden and Treatment Patterns of Cycling between Conventional Synthetic Disease-modifying Antirheumatic Drugs Among Biologic-treated Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis.Clin Ther. 2016 May;38(5):1205-16. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.03.013. Epub 2016 Apr 2. Clin Ther. 2016. PMID: 27045991
-
Rheumatoid arthritis and risk of acute myocardial infarction--a nationwide retrospective cohort study.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Oct 12;168(5):4750-4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.07.233. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23938220
-
Increased Risk of Acute Pancreatitis in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Population-Based Cohort Study.PLoS One. 2015 Aug 11;10(8):e0135187. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135187. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26262880 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep disorders associated with risk of rheumatoid arthritis.Sleep Breath. 2018 Dec;22(4):1083-1091. doi: 10.1007/s11325-018-1639-1. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Sleep Breath. 2018. PMID: 29428977
-
A systematic review of validated methods for identifying patients with rheumatoid arthritis using administrative or claims data.Vaccine. 2013 Dec 30;31 Suppl 10:K41-61. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.03.075. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 24331074 Review.
Cited by
-
Hydroxychloroquine Does Not Increase the Risk of Cardiac Arrhythmia in Common Rheumatic Diseases: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 2;12:631869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.631869. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868251 Free PMC article.
-
Hair Disorders in Autoimmune Diseases.Skin Appendage Disord. 2023 Mar;9(2):84-93. doi: 10.1159/000527933. Epub 2023 Jan 24. Skin Appendage Disord. 2023. PMID: 36937160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quality of Life and the Presence of Depression Among Adults with Hair Loss in the South of Saudi Arabia.Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2022 Aug 4;15:1989-1996. doi: 10.2147/PRBM.S375247. eCollection 2022. Psychol Res Behav Manag. 2022. PMID: 35957760 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between ABO and Rh Blood Groups with Alopecia Areata.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023 Jan 1;13(1):e2023060. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1301a60. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023. PMID: 36892374 Free PMC article.
-
Association between genetically predicted rheumatoid arthritis and alopecia areata: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 31;14:1269640. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1269640. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022630 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources