Staining and Quantification of β-Amyloid Pathology in Transgenic Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 32410038
- PMCID: PMC7299244
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0592-9_19
Staining and Quantification of β-Amyloid Pathology in Transgenic Mouse Models of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Studies of Alzheimer's disease (AD) using experimental systems most often involve transgenic mouse models that are characterized by neural accumulation of β-amyloid protein (Aβ), which is widely hypothesized to have a key role in AD pathogenesis. Quantification of Aβ in transgenic mice typically is accomplished through both biochemical and histochemical approaches. In this chapter, we describe two techniques for the histological detection of Aβ, immunostaining with Aβ antibodies and staining with the amyloid dye thioflavin S, and its quantification using digital imaging.
Keywords: Immunohistochemistry; Quantitative imaging; Thioflavin S; Transgenic mice; β-Amyloid.
Figures
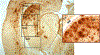
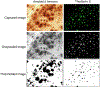
Similar articles
-
Fibrillar Aβ triggers microglial proteome alterations and dysfunction in Alzheimer mouse models.Elife. 2020 Jun 8;9:e54083. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54083. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32510331 Free PMC article.
-
Intraneuronal Abeta accumulation precedes plaque formation in beta-amyloid precursor protein and presenilin-1 double-transgenic mice.Neurosci Lett. 2001 Jun 22;306(1-2):116-20. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(01)01876-6. Neurosci Lett. 2001. PMID: 11403971
-
N-truncated Aβ4-x peptides in sporadic Alzheimer's disease cases and transgenic Alzheimer mouse models.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017 Oct 4;9(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13195-017-0309-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2017. PMID: 28978359 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid precursor protein transgenic mouse models and Alzheimer's disease: understanding the paradigms, limitations, and contributions.Alzheimers Dement. 2009 Jul;5(4):340-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2009.03.002. Alzheimers Dement. 2009. PMID: 19560104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress toward valid transgenic mouse models for Alzheimer's disease.Neurobiol Aging. 1999 Mar-Apr;20(2):201-11. doi: 10.1016/s0197-4580(99)00042-1. Neurobiol Aging. 1999. PMID: 10537029 Review.
Cited by
-
Age-Dependent Sex Differences in Perineuronal Nets in an APP Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease Are Brain Region-Specific.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 5;24(19):14917. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914917. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834366 Free PMC article.
-
Full- versus Sub-Regional Quantification of Amyloid-Beta Load on Mouse Brain Sections.J Vis Exp. 2022 May 19;(183):10.3791/63669. doi: 10.3791/63669. J Vis Exp. 2022. PMID: 35661689 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Purinergic P2 Receptors in the Mouse Hippocampus.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 28;22(15):8078. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158078. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360844 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of PLK2 kinase activity mitigates cognitive decline but aggravates APP pathology in a sex-dependent manner in APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 18;10(20):e39571. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39571. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39498012 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressing UBE2N ameliorates Alzheimer's disease pathology through the clearance of amyloid beta.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Sep;20(9):6287-6304. doi: 10.1002/alz.14122. Epub 2024 Jul 17. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39015037 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vinters HV (2015) Emerging concepts in Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Pathol 10:291–319 - PubMed
-
- Bloom GS (2014) Amyloid-β and tau: the trigger and bullet in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. JAMA Neurol 71:505–508 - PubMed
-
- Sala Frigerio C, De Strooper B (2016) Alzheimer’s disease mechanisms and emerging roads to novel therapeutics. Annu Rev Neurosci 39:57–79 - PubMed
-
- Schmidt SD, Mazzella MJ, Nixon RA, Mathews PM (2012) Aβ measurement by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Methods Mol Biol 849:507–527 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

