Robustness of a biomolecular oscillator to pulse perturbations
- PMID: 32406377
- PMCID: PMC8687342
- DOI: 10.1049/iet-syb.2019.0029
Robustness of a biomolecular oscillator to pulse perturbations
Abstract
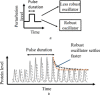
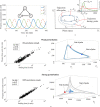
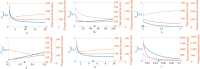
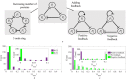
Biomolecular oscillators can function robustly in the presence of environmental perturbations, which can either be static or dynamic. While the effect of different circuit parameters and mechanisms on the robustness to steady perturbations has been investigated, the scenario for dynamic perturbations is relatively unclear. To address this, the authors use a benchmark three protein oscillator design - the repressilator - and investigate its robustness to pulse perturbations, computationally as well as use analytical tools of Floquet theory. They found that the metric provided by direct computations of the time it takes for the oscillator to settle after pulse perturbation is applied, correlates well with the metric provided by Floquet theory. They investigated the parametric dependence of the Floquet metric, finding that the parameters that increase the effective delay enhance robustness to pulse perturbation. They found that the structural changes such as increasing the number of proteins in a ring oscillator as well as adding positive feedback, both of which increase effective delay, facilitates such robustness. These results highlight such design principles, especially the role of delay, for designing an oscillator that is robust to pulse perturbation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analytical study of robustness of a negative feedback oscillator by multiparameter sensitivity.BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8 Suppl 5(Suppl 5):S1. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-8-S5-S1. Epub 2014 Dec 12. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25605374 Free PMC article.
-
Incoherent Inputs Enhance the Robustness of Biological Oscillators.Cell Syst. 2017 Jul 26;5(1):72-81.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2017.06.013. Cell Syst. 2017. PMID: 28750200 Free PMC article.
-
A method for determining the robustness of bio-molecular oscillator models.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 Sep 21;3:95. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-95. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19772565 Free PMC article.
-
Pulse coupled oscillators and the phase resetting curve.Math Biosci. 2010 Aug;226(2):77-96. doi: 10.1016/j.mbs.2010.05.001. Epub 2010 May 10. Math Biosci. 2010. PMID: 20460132 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian circadian signaling networks and therapeutic targets.Nat Chem Biol. 2007 Oct;3(10):630-9. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.37. Nat Chem Biol. 2007. PMID: 17876320 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

