Orf Virus-Based Therapeutic Vaccine for Treatment of Papillomavirus-Induced Tumors
- PMID: 32404527
- PMCID: PMC7375371
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00398-20
Orf Virus-Based Therapeutic Vaccine for Treatment of Papillomavirus-Induced Tumors
Abstract
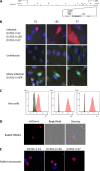
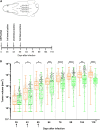
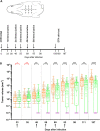
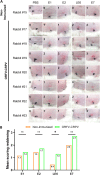
Orf virus (ORFV) represents a suitable vector for the generation of efficient, prophylactic antiviral vaccines against different pathogens. The present study investigated for the first time the therapeutic application of ORFV vector-based vaccines against tumors induced by cottontail rabbit papillomavirus (CRPV). ORFV-CRPV recombinants were constructed expressing the early CRPV gene E1, E2, E7, or LE6. In two independent experiments we used in total 23 rabbits which were immunized with a mixture of the four ORFV-CRPV recombinants or empty ORFV vector as a control 5 weeks after the appearance of skin tumors. For the determination of the therapeutic efficacy, the subsequent growth of the tumors was recorded. In the first experiment, we could demonstrate that three immunizations of rabbits with high tumor burden with the combined four ORFV-CRPV recombinants resulted in significant growth retardation of the tumors compared to the control. A second experiment was performed to test the therapeutic effect of 5 doses of the combined vaccine in rabbits with a lower tumor burden than in nonimmunized rabbits. Tumor growth was significantly reduced after immunization, and one vaccinated rabbit even displayed complete tumor regression until the end of the observation period at 26 weeks. Results of delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) skin tests suggest the induction of a cellular immune response mediated by the ORFV-CRPV vaccine. The data presented show for the first time a therapeutic potential of the ORFV vector platform and encourage further studies for the development of a therapeutic vaccine against virus-induced tumors.IMPORTANCE Viral vectors are widely used for the development of therapeutic vaccines for the treatment of tumors. In our study we have used Orf virus (ORFV) strain D1701-V for the generation of recombinant vaccines expressing cottontail rabbit papillomavirus (CRPV) early proteins E1, E2, LE6, and E7. The therapeutic efficacy of the ORFV-CRPV vaccines was evaluated in two independent experiments using the outbred CRPV rabbit model. In both experiments the immunization achieved significant suppression of tumor growth. In total, 84.6% of all outbred animals benefited from the ORFV-CRPV vaccination, showing reduction in tumor size and significant tumor growth inhibition, including one animal with complete tumor regression without recurrence.
Keywords: CRPV; ORFV; Orf virus; cottontail rabbit papillomavirus; papillomavirus; therapeutic vector vaccine.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vesicular stomatitis virus-based therapeutic vaccination targeted to the E1, E2, E6, and E7 proteins of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus.J Virol. 2007 Jun;81(11):5749-58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02835-06. Epub 2007 Mar 28. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17392369 Free PMC article.
-
Intracutaneous DNA vaccination with the E8 gene of cottontail rabbit papillomavirus induces protective immunity against virus challenge in rabbits.J Virol. 2002 Jul;76(13):6453-9. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.13.6453-6459.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12050357 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant Listeria monocytogenes vaccination eliminates papillomavirus-induced tumors and prevents papilloma formation from viral DNA.J Virol. 1997 Nov;71(11):8467-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.11.8467-8474.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9343203 Free PMC article.
-
Cottontail rabbit papillomavirus (CRPV) model system to test antiviral and immunotherapeutic strategies.Antivir Chem Chemother. 2005;16(6):355-62. doi: 10.1177/095632020501600602. Antivir Chem Chemother. 2005. PMID: 16331841 Review.
-
Modeling HPV-Associated Disease and Cancer Using the Cottontail Rabbit Papillomavirus.Viruses. 2022 Sep 4;14(9):1964. doi: 10.3390/v14091964. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Orf Virus-Based Vectors Preferentially Target Professional Antigen-Presenting Cells, Activate the STING Pathway and Induce Strong Antigen-Specific T Cell Responses.Front Immunol. 2022 May 9;13:873351. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.873351. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35615366 Free PMC article.
-
The cooperation between orf virus and Staphylococcus aureus leads to intractable lesions in skin infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jan 8;13:1213694. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1213694. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38259972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A replicative recombinant HPV16 E7 expression virus upregulates CD36 in C33A cells.Front Microbiol. 2023 Aug 30;14:1259510. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1259510. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37795297 Free PMC article.
-
Orf Virus-Based Vaccine Vector D1701-V Induces Strong CD8+ T Cell Response against the Transgene but Not against ORFV-Derived Epitopes.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Jun 10;8(2):295. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8020295. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32531997 Free PMC article.
-
Oncolytic Parapoxvirus induces Gasdermin E-mediated pyroptosis and activates antitumor immunity.Nat Commun. 2023 Jan 14;14(1):224. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-35917-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36641456 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

