Persistent Roseoloviruses Infection in Adult Patients with Epilepsy
- PMID: 32403392
- PMCID: PMC7288180
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10050287
Persistent Roseoloviruses Infection in Adult Patients with Epilepsy
Abstract
Background: Human herpesviruses (HHV)-6A, HHV-6B and HHV-7 are considered to be involved in the pathogenesis of epilepsy, a common neurological disorder. The objective of this study was to determine the association of roseoloviruses infection with epilepsy.
Methods: 53 epilepsy patients and 104 ordinary blood donors were analyzed to determine presence of virus-specific antibodies by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and immunofluorescence assay (IFA), genomic sequences, viral load and gene expression by polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) and restriction analysis, HHV-6 protein expression by IFA and level of cytokines by ELISA.
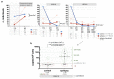
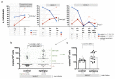
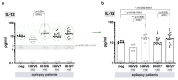
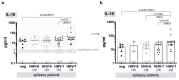
Results: Roseoloviruses genomic sequences in DNA samples from whole blood were found in 86.8% of patients versus 54.8% of controls and active infection was revealed only in patients with epilepsy (19.6% of roseolovirus-positive patients). Significantly higher viral load and more frequent gene expression was detected in patients compared to the controls. HHV-6-encoded protein expression was demonstrated in 53.3% of patients with previously detected HHV-6 DNA. Changes in level of cytokines were determined in patients with elevated viral load compared to the patients without elevated viral loads and to the controls.
Conclusions: Results on frequent active HHV-6 and HHV-7 infection in epilepsy patient' peripheral blood indicate on possible involvement of these viruses in the disease development.
Keywords: epilepsy; human herpesvirus-6; human herpesvirus-7; reactivation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complete Unique Genome Sequence, Expression Profile, and Salivary Gland Tissue Tropism of the Herpesvirus 7 Homolog in Pigtailed Macaques.J Virol. 2016 Jul 11;90(15):6657-6674. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00651-16. Print 2016 Aug 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27170755 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitation of human herpesvirus-6A, -6B and -7 DNAs in whole blood, mononuclear and polymorphonuclear cell fractions from healthy blood donors.J Clin Virol. 2012 Feb;53(2):151-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2011.10.017. Epub 2011 Nov 30. J Clin Virol. 2012. PMID: 22133730
-
Association of human herpesvirus-6B with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy.PLoS Med. 2007 May;4(5):e180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040180. PLoS Med. 2007. PMID: 17535102 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical impact of primary infection with roseoloviruses.Curr Opin Virol. 2014 Dec;9:91-6. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2014.09.013. Epub 2014 Oct 14. Curr Opin Virol. 2014. PMID: 25462439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Human herpes virus 6 infection in renal transplant recipient--case report].Przegl Epidemiol. 2006;60(1):141-6. Przegl Epidemiol. 2006. PMID: 16758753 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Evasion of the Host Immune Response by Betaherpesviruses.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 13;22(14):7503. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147503. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299120 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fisher R.S., Boas W.V., Blume W., Elger C., Genton P., Lee P., Engel J., Jr. Epileptic seizures and epilepsy: Definitions proposed by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE) and the International Bureau for Epilepsy (IBE) Epilepsia. 2005;46:470–472. doi: 10.1111/j.0013-9580.2005.66104.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

